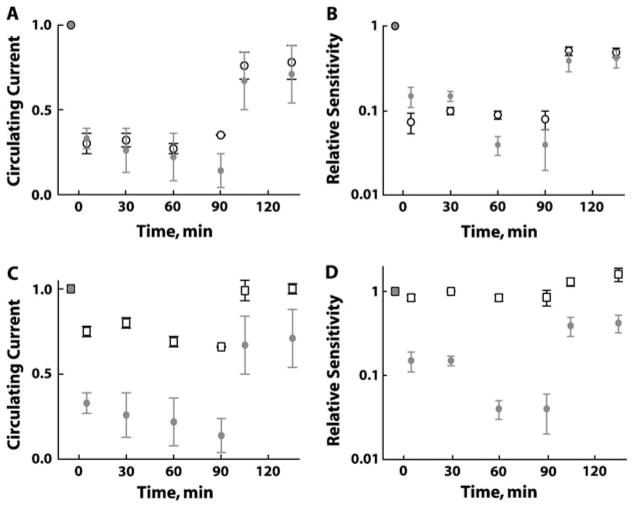
Fig. 4.
Comparison of treatments with β-ionone to steady light at 500 nm (9–33 × 102 photons/μm2/s). (A) Steady light (open black circles; 30.7 ± 5% of control, n = 3) and perfusion with 58–67 μM β-ionone (gray circles; 31.5 ± 5% of control, n = 4) each suppressed initially ~70% of the circulating current in BS rods. When light or β-ionone was turned off following 100+ min, recovery of circulating current was incomplete, indicating bleaching of visual pigment in both cases. (B) β-Ionone (gray circles) and steady light (open black circles) each decreased sensitivity to flashes and caused a measurable loss of sensitivity after cessation of treatment. High concentrations of β-ionone (52–58 μM) suppressed less circulating current in GS rods (C, open squares, n = 5) and had no effect on relative sensitivity (D, open squares, n= 5); gray circles are the corresponding BS rod data from (A) and (B), respectively. Error bars represent SEM. SEM, standard error of mean.