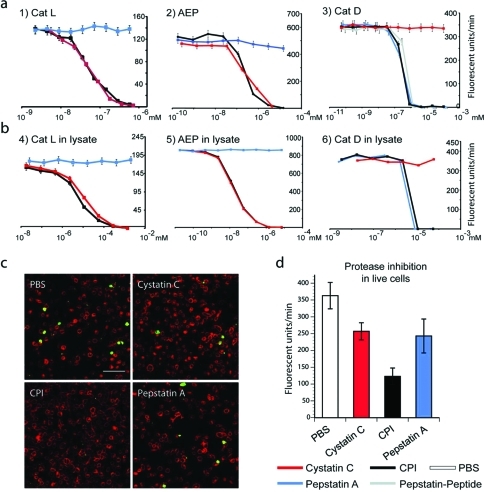
Figure 3.
(a) Residual protease activity in fluorescence units per minute of recombinant cathepsin L, AEP, and cathepsin D in the presence of varying concentrations of CPI, cystatin, or pepstatin as measured using fluorescent substrates specific for each protease. (b) Residual activity of the same enzymes as measured in lysates derived from dendritic cells using the same fluorescent substrates as in panel a. Note that only CPI inhibits all 3 protease activities. (c) Fluorescence microscopy of quenched casein substrate (Enzcheck). Upon hydrolysis, the Enzcheck fluorophore is dequenched and emits green fluorescence, indicating protease activity. A20 antigen-presenting cells (APCs) were incubated with the Enzcheck substrate and treated in the absence or presence of CPI, cystatin, or pepstatin. Representative images of fixed cells immuno-stained for the late endosomal marker CD63 (red) are shown (scale bar, 10 μm). (d) Quantification of initial rates of Enzcheck fluorescence emergence in live A20 cells as measured on an Envision fluorimeter. Quenched Bodipy-casein (Enzcheck) was incubated with A20 cells in the presence or absence of CPI, cystatin C. Error bars represent SD based on a representative experiment performed in triplicate.