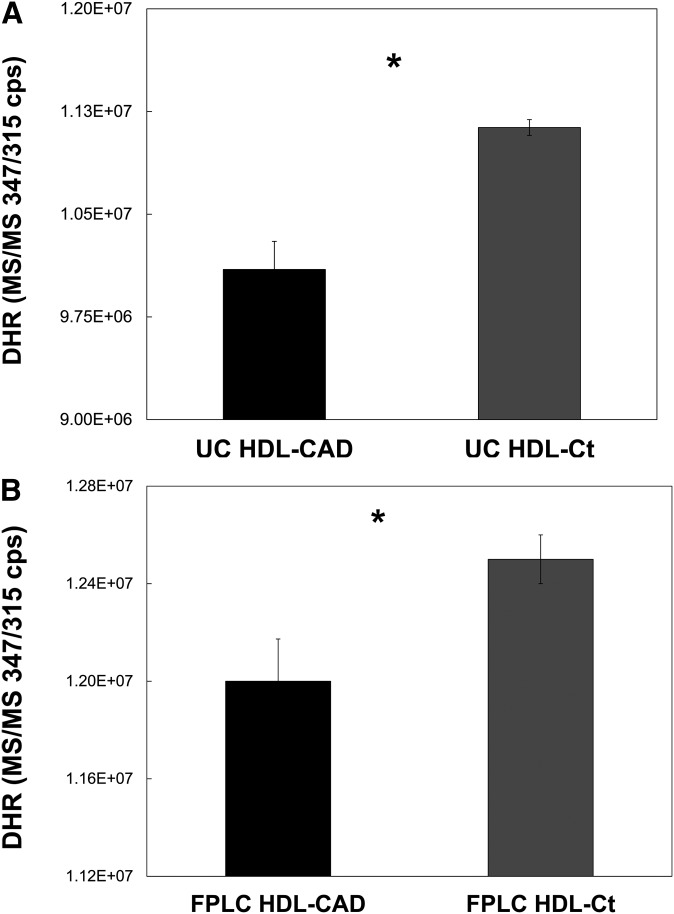
Fig.2.
HDL from healthy donors significantly inhibits the oxidation of DHR compared with HDL from CAD patients, as determined by LC/MS/MS. HDL was isolated from the serum of healthy and CAD-patient donors by either sequential UC or FPLC. Control (non-CAD) and CAD HDL pairs (HDL-CAD and HDL-Ct), one for each method of isolation, were combined in triplicate with DHR and incubated in the dark for 2 h. Each sample contained 2.5 µg HDL and 50 µM DHR in 175 total µl HEPES-buffered saline. After the incubation, urate was added (0.025 mM final concentration) to slow the further oxidation of DHR. The amount of DHR remaining in each sample was then determined by LC/MS/MS. For both the HDL-CAD and HDL-Ct pair isolated by UC (A) and the pair isolated by FPLC (B), the samples of the HDL-Ct contained significantly more DHR than the samples of the HDL-CAD (*P = 0.001, n = 3).