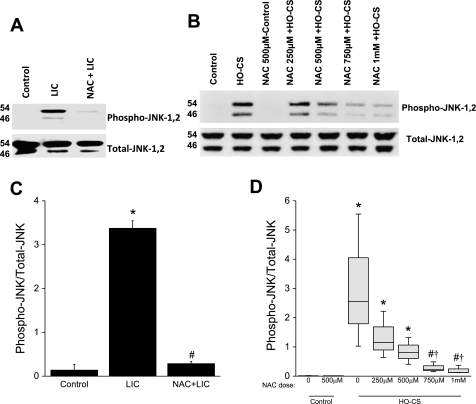
Fig. 6.
A: phosphorylation of JNK in mice subjected to control (lane 1), LIC (lane 2), and NAC + LIC (lane 3). n = 3 Mice per group. Phosphorylation of JNK was significantly increased in LIC. In NAC + LIC, phosphorylation of JNK was significantly inhibited. B: phosphorylation of JNK in MLE-12 cells subjected to control (lane 1), NAC + control (lane 3), LIC (lane 2), and NAC + HO-CS at several different doses; HO-CS + 200 μM NAC (lane 4), 500 μM NAC (lane 5), 750 μM NAC (lane 6), and 1 mM NAC (lane 7). JNK phosphorylation was observed in HO-CS, and a dose-dependent inhibition of JNK phosphorylation was observed in HO-CS + NAC. C: densitometry for phospho-JNK Western blots from whole lung homogenates. NAC treatment significantly inhibited phospho-JNK in vivo. D: box plots for densitometry of phospho-JNK Western blots from MLE-12 cell lysates. Horizontal lines indicate median, shaded boxes indicate inner quartile, and whiskers indicate data range. In these in vitro experiments, a dose-dependent inhibition of JNK phosphorylation was observed with NAC treatment. n = 3 Mice per group (in vivo) and 3 independent experiments in which 4 wells were pooled for each condition (in vitro). *P < 0.05 compared with control. #P < 0.05 compared with LIC (in vivo) or HO-CS (in vitro). †P < 0.05 compared with HO-CS 250 μM NAC.