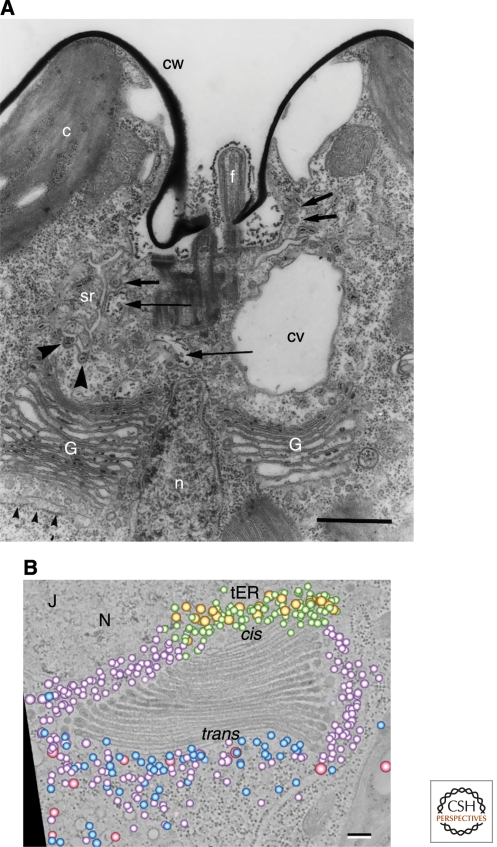
Figure 6.
Two views of Golgi stacks in the alga Scherffelia dubia. (A) Thin-section electron micrograph of the apical region of a S. dubia cell. The two Golgi stacks (G) are separated by the nucleus (n). Small arrowheads indicate the transitional ER, which is the site of ER exit. Electron-dense scales can be seen in Golgi cisternae but not in peri-Golgi vesicles. Scale bar, 1.0 µm. (Panel A adapted from Perasso et al. [2000] and reprinted with permission from Springer ©2000.) (B) An electron tomographic slice of a single S. dubia Golgi stack next to a transitional ER site (tER). Superimposed on this slice is a 3D model of the Golgi-associated vesicles, which were interpreted as falling into five classes: two morphologically distinct classes of COPI vesicles (purple and green), COPII vesicles (gold), secretory vesicles (blue), and clathrin-coated vesicles (pink). Scale bar, 100 nm. (Panel B reproduced, with permission, from Staehelin and Kang [2008].)