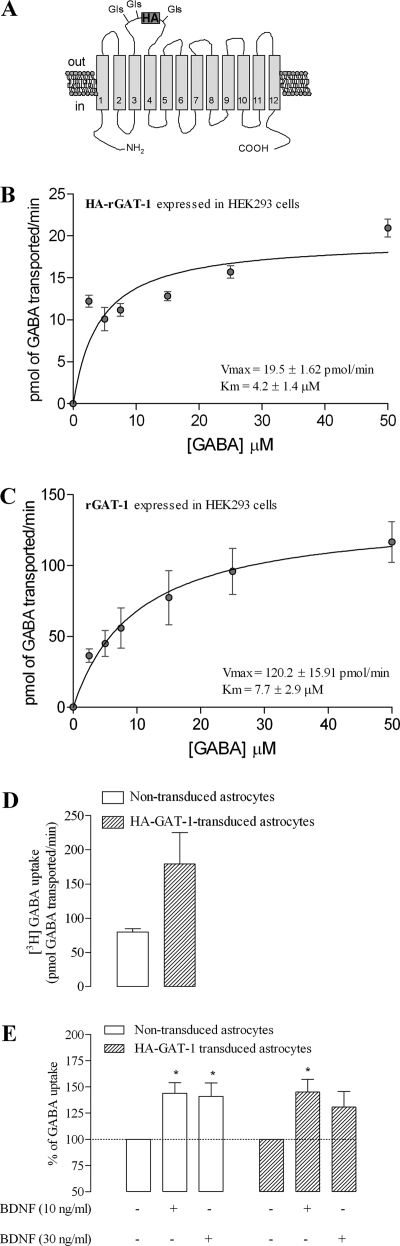
FIGURE 4.
Characterization of HA-GAT-1-mediated GABA transport. A, schematic representation of the localization of the HA tag, which was placed in EL2 of rat GAT-1; predicted N-glycosylation sites in the EL2 are indicated. B and C, saturation kinetics of GAT-1-mediated GABA uptake in HEK293 cells stably expressing HA-GAT-1 (B) or rGAT-1 (C). The Km and Vmax values are shown as an inset in the corresponding graph. D, [3H]GABA uptake through GAT-1 in HA-GAT-1-transduced (filled bars) and non-transduced (open bars) astrocytes. E, BDNF effects on GABA uptake in HA-rGAT-1-transduced (filled bars) and non-transduced (open bars) astrocytes from the same cell batch. The ordinates represent the [3H]GABA uptake as a percentage of the control value (no BDNF added) in the same experiment and in the same cell batch in similar conditions. In all panels, the results are expressed as mean ± S.E. (error bars) from three (B), two (C and D), or five (E) independent experiments. *, p < 0.05 (one-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post-test) as compared with control (no drug added, first column on the left) in the same group of cells.