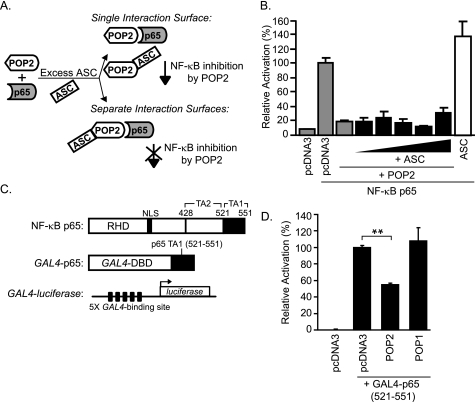
FIGURE 5.
POP2 inhibits NF-κB p65 independently of ASC by interfering with NF-κB p65 transactivation. A, schematic showing two functional outcomes of ASC overexpression upon POP2-mediated inhibition of NF-κB p65. B, NF-κB luciferase assay in 293T cells, as described in the legend for Fig. 3, in the absence or presence of increasing amounts of transfected ASC (100 ng-2 μg). The result shown is representative of two experiments (error bars, S.D.). C, schematic of full-length NF-κB p65(1–551) with Rel homolgy domain (RHD) and transactivation (TA) domains 1 and 2; GAL4-p65(521–551) fusion construct containing the DNA-binding domain (DBD) of GAL4 and the TA1 of NF-κB p65; and GAL4-luciferase construct containing five tandem repeats of GAL4-binding site upstream of firefly luciferase. D, GAL4-luciferase assay in 293 cells transfected with pcDNA3 control, POP1, or POP2. Results are represented as percentage luciferase activity and shown as mean ± S.D. of one representative experiment of 3–4 independent transfections giving similar results (**, p < 0.001).