FIGURE 7.
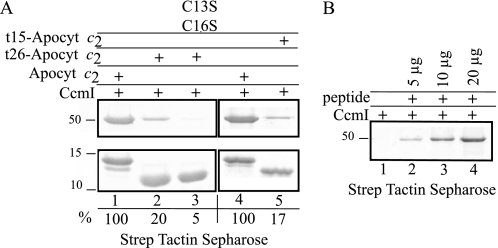
CcmI interacts directly with the C-terminal portion of apocytochrome c2. Panel A, co-purification of His10-CcmI with full-length and C-terminal-truncated derivatives t15- and t26- apocytochrome c2 and appropriate double Cys mutants is shown. Co-purification was done as in Fig. 3, panel B, except that His10-CcmI (5 μg) was incubated with apocytochrome c2 (Apocyt c2, 15 μg) or the appropriate derivatives as before. Lanes 1 and 4 show co-purification of CcmI with full-length apocytochrome c2, and the amount of CcmI present in the elution fraction was taken as 100% for image quantification as in Fig. 6. The amount of CcmI present in the elution fraction after incubation with t26-apocytochrome c2 was decreased to 20% as compared with the full-length apocytochrome c2 (lane 2). Lane 3 shows that after mutation of the Cys residues of t26-apocytochrome c2, the amount of CcmI that co-purifies is barely detectable. The amount of CcmI present in the elution fraction after incubation with t15-apocytochrome c2 (lane 5) was also decreased to 17% as compared with the full-length apocytochrome c2 shown in lane 4, similar to that seen with the t26-apocytochrome c2 (lane 2). Panel B, co-purification of His10-CcmI using different amounts of a synthetic peptide corresponding to the C-terminal 26-amino acid residues of apocytochrome c2 is shown. Lane 1 shows that His10-CcmI is not retained by the Strep Tactin resin in the absence of the synthetic peptide, and increasing amounts of His10-CcmI co-purified with 5, 10, and 20 μg (lanes 2, 3, and 4, respectively) of the synthetic peptide.