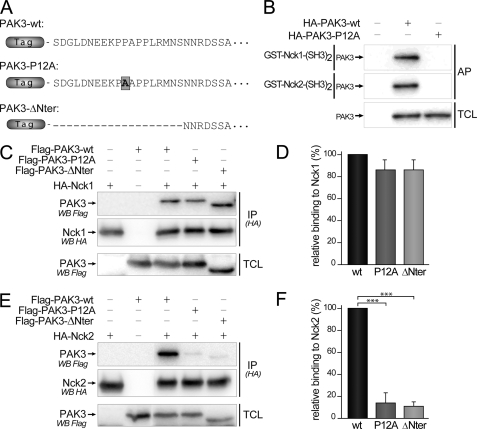
FIGURE 6.
Mutation of the proline 12 residue and deletion of the N-terminal part of PAK3 suppress co-immunoprecipitation with Nck2 but not with Nck1. A, amino acid sequences of the N-terminal extremity of mouse PAK3 protein and the two mutated proteins used in this study. B, P12A mutation impairs the affinity precipitation of PAK3 protein with the second SH3 domains of Nck1 and Nck2 fused to GST. C, mutation of the proline 12 in PAK3 does not significantly change the interaction with Nck1. FLAG-PAK3 wild-type (wt), with the mutation P12A (P12A) or deleted for the first 20 amino acids (ΔNter) were co-expressed with HA-Nck1 in COS-7 cells. Nck1 protein was HA-immunoprecipitated and the presence of PAK3 in precipitated complexes (IP(HA)) and in TCLs was analyzed by Western blotting (WB) with FLAG antibodies. The amount of Nck1 precipitated proteins was controlled by anti-HA immunoblotting. D, relative binding of PAK3 proteins to Nck1, quantified from three independent experiments illustrated from C and averaged. E, mutation of the proline 12 in PAK3 abolished the interaction with Nck2. PAK3 proteins were co-expressed with HA-Nck2 in COS-7 cells. Nck2 protein was HA-immunoprecipitated and the presence of PAK3 in precipitated complexes (IP(HA)) and in TCL was analyzed by Western blotting with FLAG antibodies. The amount of Nck2 precipitated proteins was controlled by anti-HA immunoblotting. F, relative binding of PAK3 proteins to Nck2, quantified from four independent experiments illustrated from E. Comparison with Student's t test: ***, p < 0.001, n = 3. Errors bars indicate the S.E.