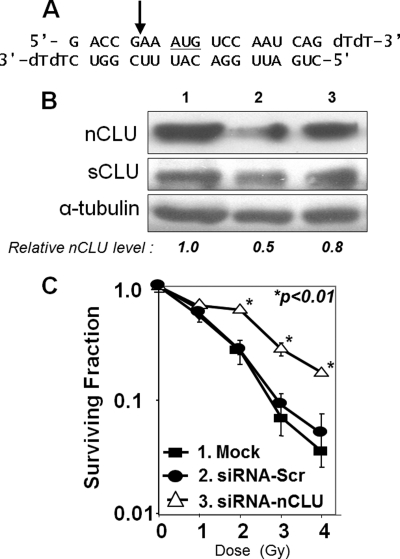
FIGURE 1.
nCLU knockdown creates IR-resistant MCF-7 cells. A, sequence of double strand siRNA-nCLU. The AUG translational start site for nCLU protein is underlined. The arrow indicates the exon I/III junction that results from nCLU-specific alternative splicing (8). B, changes in nCLU and sCLU protein levels in MCF-7 cells 60 h after transfection with siRNA-nCLU. MCF-7 cells were transfected as follows: lane 1, mock-transfected cells; lane 2, siRNA-nCLU, siRNA selective for nCLU and the exon I/III junction (arrow, A); and lane 3, siRNA-Scr, siRNA 21-oligomer generated to a nonspecific sequence in the human genome. nCLU, sCLU, and α-tubulin steady-state protein levels were monitored by Western blot analyses. The blot shown is representative of experiments performed three or more times. C, MCF-7 cells transfected with siRNA-nCLU and resistant to IR. MCF-7 cells were transfected with siRNA-nCLU (open triangles), siRNA-Scr (filled circles), and mock-siRNA (filled squares) as described under “Experimental Procedures.” Colony forming assays were performed on transfectants as described under “Experimental Procedures.” An increase in the surviving fraction of siRNA-nCLU-transfected MCF-7 cells after exposure to 2–4 Gy versus mock- or scramble-siRNA-transfected cells was noted (p < 0.01).