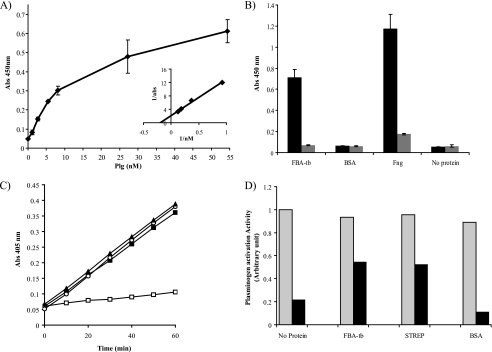
FIGURE 4.
Human Plg binding properties of FBA-tb: impact on Plg activation and regulation of plasmin by α2-antiplasmin. A, binding of human Plg to FBA-tb measured by ELISA over a range of Plg concentrations (see “Experimental Procedures”). The inset shows a double reciprocal plot of 1/bound (1/A450 nm) against 1/[Plg] used to determine the Kd. Each point was measured in triplicate, and the mean values and S.D. (error bars) are shown. B, the binding of human Plg (5 μg) to FBA-tb, fibrinogen (Fng) (positive control), BSA (negative control), or no protein was determined by ELISA in the presence (gray bars) and absence (black bars) of ϵ-aminocaproic acid (50 mm). 2 μg of FBA-tb, fibrinogen, or BSA coated each well. C, the activation of Plg into plasmin in the presence or absence of tPA was measured in the presence of fibrin matrices using Chromozym as the substrate (see “Experimental Procedures”). The complete reaction mixture contained FBA-tb (2 μg), Plg (1 μg), and tPA (0.025 μg) (filled squares). In some assays, tPA was omitted from the reaction mixture (open squares), no FBA-tb or streptokinase was present (open circles), or streptokinase (0.0875 units; 24 ng) replaced FBA-tb (filled triangles). No tPA was present in the wells containing streptokinase. Each point was measured in triplicate, and the mean values and S.D. (error bars) are shown. The values obtained in the FBA-tb assays lacking Plg were similar to those obtained when tPA was omitted. D, regulation of plasmin activity by α2-antiplasmin. Plasmin activity was measured in the presence of fibrin matrices, Plg, and tPA as described in C and in the absence (gray bars) or presence (black bars) of α2-antiplasmin (2 μg). FBA-tb (2 μg) or BSA (2 μg) was added to some wells at the same time as Plg (see “Experimental Procedures”). Wells containing streptokinase (STREP) (0.0875 units; 24 ng) did not contain tPA. Protease activity was calculated from the slopes of kinetic assays performed in duplicate for each condition (see C), and all values were expressed relative to the reaction rate measured for the “no protein/no α2-antiplasmin” control well arbitrarily set to 1. No protease activity was detected in the presence of ϵ-aminocaproic acid (75 mm) in the reaction mixture. Abs, absorbance.