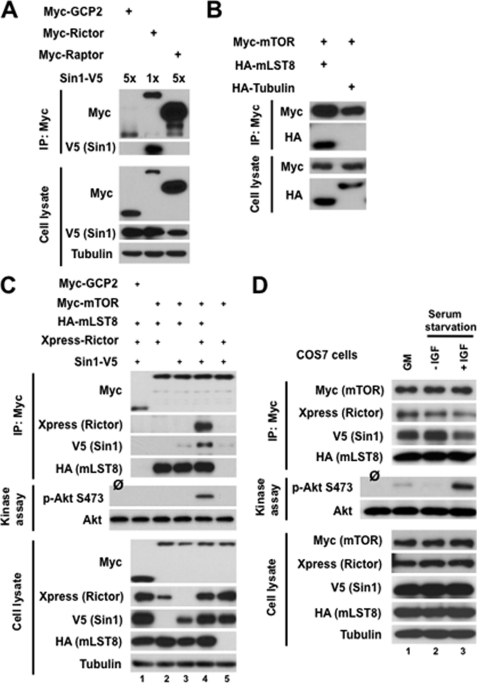
FIGURE 1.
Reconstitution of the functional mTORC2 complex by expressing its recombinant components. A, rictor interacts with SIN1. SIN1-V5 plasmid DNA was co-transfected with myc-rictor into HEK-293T cells by Lipofectamine 2000, and cells were analyzed 48 h following transfection. Cell lysates were applied for immunoprecipitation (IP) with anti-myc antibody. The immunoprecipitates and cell lysates were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-myc and anti-V5 antibodies. First and third lanes, negative controls are presented by expressing myc-GCP2 or myc-raptor with SIN1-V5. B, mTOR interacts with mLST8. Myc-mTOR construct was co-transfected with HA-mLST8 in HEK-293T cells and analyzed as in A. Right 2, a negative control is presented by expressing HA-α-tubulin with myc-mTOR. C, interaction of mTOR with other mTORC2 components. The differently tagged recombinant components of mTORC2 were transiently expressed in HEK-293T cells, and the assembled complexes were purified by the immunoprecipitation of myc-mTOR. Lane 1, a negative control is presented by expressing myc-GCP2 with SIN1-V5, Xp-rictor, and HA-mLST8. D, reconstituted mTORC2 kinase activity was stimulated by IGF-1. The differently tagged recombinant components of mTORC2 were transiently expressed in COS-7 cells, and the assembled complexes were purified by the immunoprecipitation of myc-mTOR. Lane 1, COS-7 cells expressing recombinant mTORC2 were cultured in growth medium containing 10% serum. Lanes 2 and 3, COS-7 cells expressing recombinant mTORC2 were cultured in serum-free medium for 16 h and then treated without or with IGF-I (100 ng/ml) for 30 min, respectively.