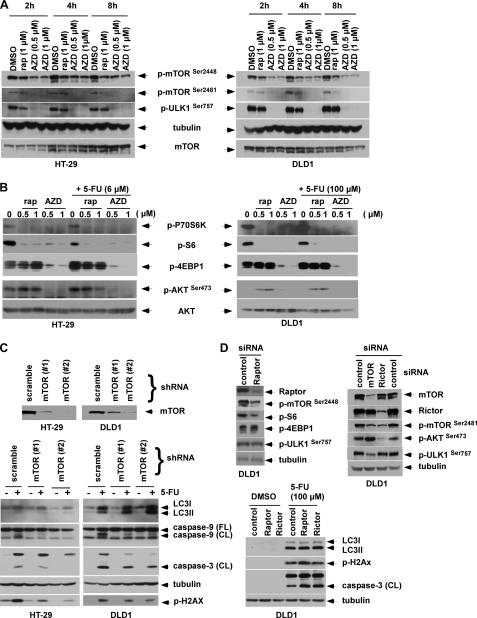
FIGURE 7.
AZD8055 inhibits ULK1 phosphorylation at Ser757 and blocks mTORC1/mTORC2 downstream signaling. A, cells were treated with rapamycin (rap) or AZD8055 (AZD) for the indicated doses and times, and p-mTOR (Ser2448 and Ser2481) and p-ULK1 (Ser757) were analyzed in whole cell lysates by immunoblotting. B, cells were treated with rapamycin or AZD8055 in the presence or absence of 5-FU for 24 h, and analysis of mTORC1 (p-P70S6K, p-S6, p-4E-BP1) and mTORC2 (p-AKT at Ser473) substrates was performed by immunoblotting. C, mTOR knockdown by shRNA is shown to potentiate 5-FU-induced autophagy, indicated by LC3I-II conversion that was associated with protection from 5-FU-induced DNA damage and apoptosis. Suppression of mTOR was achieved by transduction with two lentiviral shRNA sequences targeting mTOR (#1 or #2) compared with a scramble shRNA. Knockdown or control cells were treated with 5-FU (6 μm for HT-29, 100 μm for DLD1) for 5 days and LC3I-II conversion, DNA damage (p-H2AX) and caspase-9, -3 cleavage were probed. D, knockdown of mTOR, but not Raptor or Rictor, confers cytoprotection. DLD1 cells were transfected with mTOR, Raptor or Rictor siRNA for 3 days and phosphorylation of p-mTOR (Ser2448 and Ser2481), p-ULK1 (Ser757), as well as phosphorylation of the substrates of mTORC1 (p-S6, p-4EBP-1) or mTORC2 (p-AKT at Ser473) were analyzed. Raptor, Rictor or control knockdown cells were treated with 5-FU for 5 days, and expression of p-H2AX and caspase-9, -3 cleavage were measured.