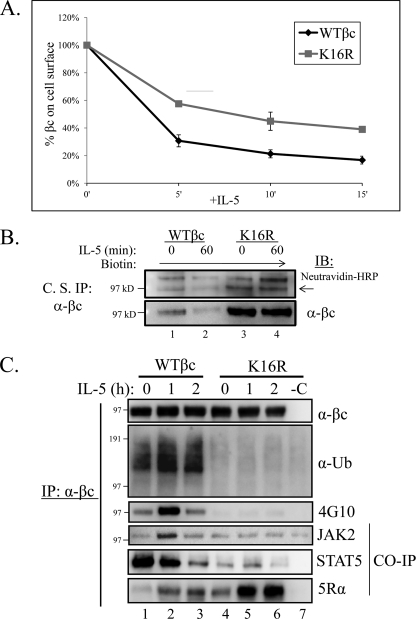
FIGURE 6.
Ubiquitination-deficient βc K16R receptors show impairment in IL-5-stimulated endocytosis and signaling. A, βc endocytosis assay. Briefly, pre-chilled HEK293 expressing WT βc and βc K16R receptors were incubated with anti-βc antibodies on ice. After washing, aliquots of cells were moved to 37 °C for the indicated time points. The remaining cell surface βc receptors were detected by incubating the anti-βc antibody-bound receptors with anti-mouse IgG1-PE and measured by flow cytometry. The MFI of immunoreactive βc receptors in both cell lines at the 0 min of IL-5 (unstimulated) was represented as 100% and the loss of immunoreactivity (MFI) was plotted for each time point (n = 3). MFIs, WT βc, 5′ = 31 ± 4%; βc K16R, 5 min = 58 ± 2%; WT βc, 10 min = 21 ± 3%; βc K16R, 10 min = 45 ± 7%; WT βc, 15 min = 17 ± 3%; βc K16R, 15 min = 39 ± 2%. B, WT βc and βc K16R-expressing HEK293 cell lines were cell surface labeled with the nonpermeable sulfo-NHS-SS-biotin reagent. Briefly, labeled cells were either left unstimulated or stimulated with 10 ng/ml of IL-5. Before cell lysis, anti-βc antibodies (BD Biosciences) were added to intact cells to bind labeled βc cell surface receptors for 2 h on ice. After cell lysis, βc immune complexes were analyzed by IB with neutravidin-HRP and anti-βc (H300) antibodies (n = 3). C, stably transduced HEK293 cells expressing WT or βc K16R receptors were stimulated with 10 ng/ml of IL-5 for the indicated times. Lysates were IP with anti-βc mAbs and analyzed by IB with the indicated antibodies. Note the correlation of lack of Ub with reduced JAK2 and STAT5 association, and Tyr phosphorylation in βc K16R receptors. n = 6.