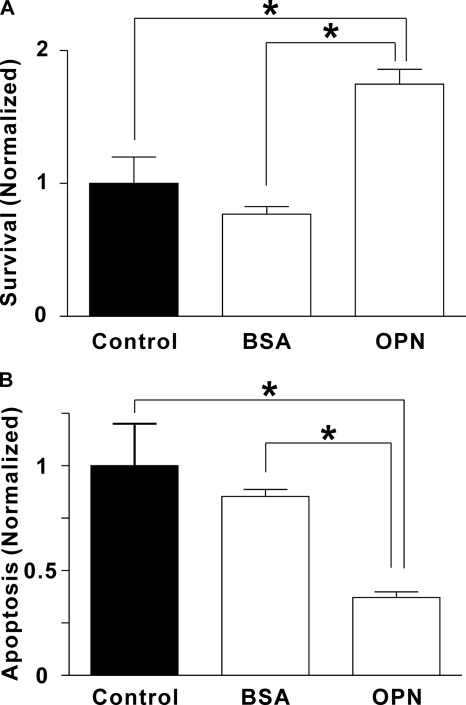
FIGURE 5.
Effects of OPN on osteoclast survival and apoptosis. Rat osteoclasts were plated on uncoated glass (Control) or substrate coated with BSA or OPN in supplemented M199 buffered with HEPES (25 mm) and HCO3− (26 mm). After a 1-h incubation at 37 °C in 5% CO2, preparations were washed to remove nonadherent cells. A, to quantify survival, we first incubated cultures for an additional 30 min to allow osteoclasts to spread. Osteoclasts were then counted, incubated 18 h at 37 °C in 5% CO2, and then counted again. The number of surviving osteoclasts on each coverslip at 18 h was expressed as a percentage of the initial number of osteoclasts on the same coverslip. Data were then normalized as a fraction of the control value. Data are mean ± S.E., n = 3 independent experiments, *, p < 0.05. On uncoated (Control) surfaces, survival was 22 ± 4%. B, to assess apoptosis, osteoclasts were incubated for 6 h at 37 °C in 5% CO2 and then stained with the DNA dye Hoechst 33342 (5 μg/ml, for at least 10 min). Osteoclasts exhibiting condensed and/or fragmented nuclei were scored as apoptotic (supplemental Fig. S3). The number of apoptotic osteoclasts was expressed as a percentage of the total number of osteoclasts in the same dish. Data were then normalized as a fraction of the control value. Data are mean ± S.E., n = 3 independent experiments, *, p < 0.05. On uncoated (Control) surfaces, apoptosis was 39 ± 8%.