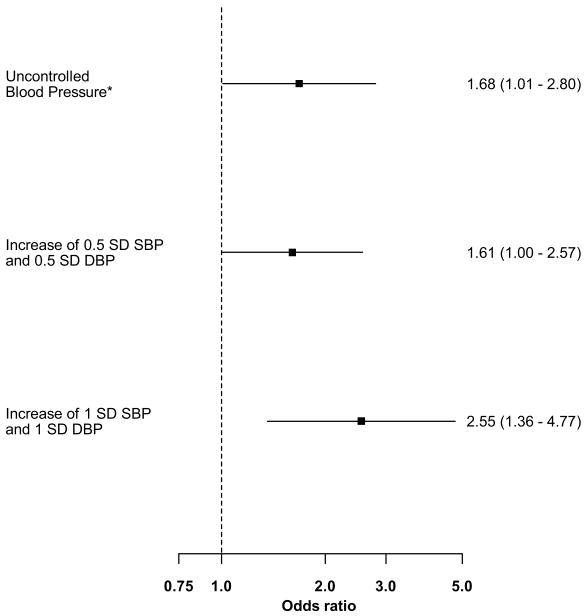
Figure 1. Decline in Medication Adherence associated with Increased Blood Pressure at Follow up.
*Uncontrolled blood pressure was defined as ≥ 140/90 at follow-up among those with controlled BP at baseline
Odds Ratios adjusted for age, gender, race, education, marital status, history of diabetes or cardiovascular disease (myocardial infarction, heart failure, cerebrovascular accident, peripheral vascular disease), number of medications, number of primary care physician visits, hypertension duration, and reduction of antihypertensive medication due to cost.
SBP-systolic blood pressure; DBP-diastolic blood pressure
SD-standard deviation
Note: 1 standard deviation of change in systolic blood pressure = 12.3 mm Hg; 1 standard deviation of change in diastolic blood pressure = 6.8 mm Hg