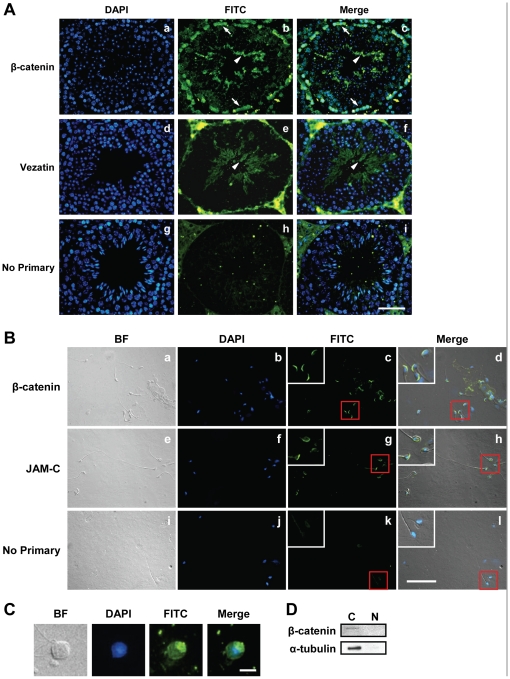
Figure 1. β-catenin is highly expressed in post-meiotic germ cells.
(A) β-catenin is expressed at the apical ectoplasmic specializations (ES) and basal compartment in testis seminiferous tubules. Testis sections were labeled with anti-β-catenin (1∶200; Sigma; panels a-c) or anti-vezatin (a protein reported to be expressed only at the apical ES [76]; 1∶200; Santa Cruz; panels d-f), followed by FITC-conjugated goat anti-rabbit secondary antibody (1∶150; Zymed). Sections were counterstained with DAPI (blue) for nuclear staining. Arrowheads indicate the apical ES, and arrows indicate the Sertoli cell/germ cell cytoplasm at the basal compartment. Scale bar, 50 µm. (B) β-catenin localization in elongated spermatids. Purified spermatids were labeled with anti-β-catenin (1∶50; Upstate; panels a-d) or anti-JAM-C (1∶50; Santa Cruz; panels e-h). Secondary antibodies were FITC-conjugated goat anti-rabbit (1∶100) for β-catenin and FITC-conjugated goat anti-rat (1∶100; Zymed) for JAM-C. Spermatids were counterstained with DAPI (blue) for nuclear staining. Areas in red boxes are magnified in insets. Scale bar, 50 µm. (C) Immunofluorescence staining of β-catenin in late round spermatids. Slides were treated as described in (B). Scale bar, 10 µm. (D) β-catenin is localized to the cytoplasm in the testis. Western blot of germ cell nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions using anti-β-catenin antibody (1∶3000; Sigma). The blot was stripped and reprobed with anti-α-tubulin (1∶2000; Sigma) to show the purity of the fractions.