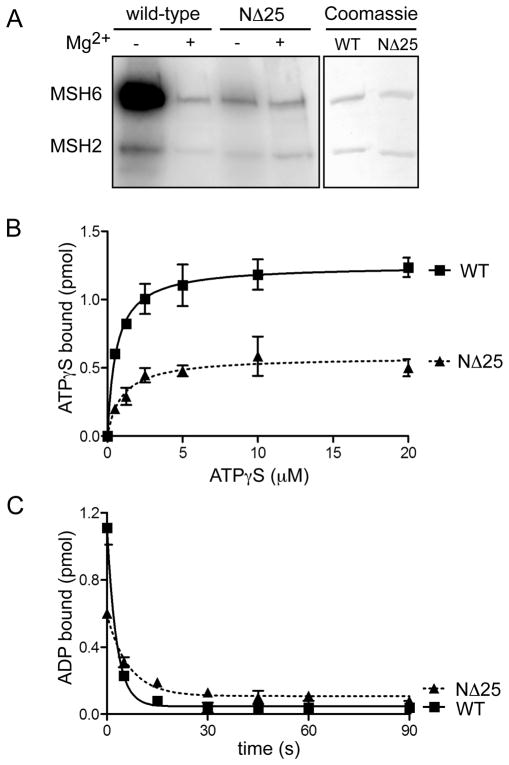
Figure 4.
Nucleotide binding and exchange properties of MSH2(NΔ25)-MSH6. (A) ATP binding activity. Wild-type MSH2-MSH6 and MSH2(NΔ25)-MSH6 proteins were UV- crosslinked to radiolabeled [γ-32P]ATP in the presence or absence of Mg2+ (to allow or inhibit hydrolysis). Radiolabeled ATP was visualized by phosphorimaging. To control for protein loading, a separate gel was equivalently loaded with each protein and Coomassie stained. (B) ATPγS binding. 100 nM of wild-type and mutant heterodimers were incubated with increasing concentrations of [35S]ATPγS. The amount of protein- bound nucleotide was determined by filter binding. (C) ADP binding and exchange for ATP. MSH2-MSH6 wild-type and mutant heterodimers were incubated with [3H]ADP. Exchange of ADP was initiated by adding mismatched DNA and excess ATP. Reactions were allowed to proceed for 0–90 seconds. The amount of ADP bound after each time point was determined by filter binding.