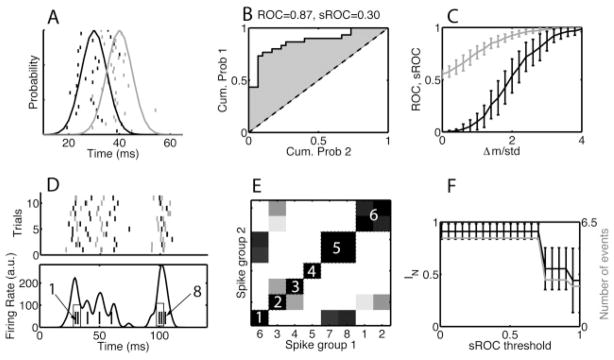
Figure 7.
The ROC-based criterion for merging events common across multiple patterns. (A) Thirty trials of (black ticks) spikes drawn from a (black curve) gaussian with a mean of 30 ms and 30 trials of (gray ticks) spikes drawn from a (gray curve) gaussian with mean 40 ms. The standard deviation of the gaussian was 5 ms for both cases. (B) The ROC curve was estimated as the cumulative distribution of the first group of spikes plotted versus that of the second group of spikes (see section 4.1.5). The ROC area was 0.87. The scaled ROC (sROC) was 0.30, which was obtained by normalizing the ROC area above the diagonal by 0.5 and taking the fourth power. (C) The same procedure was repeated for different values of the difference in means between the two distributions. We show the (gray curve) ROC and (black curve) sROC area versus the difference of theoretical means over the standard deviation (Δm/σ). We use the sROC because it is more linear near Δm/σ = 2. (D) Eleven trials of an example data set consisting of eight events, of which two sets should be merged based on the criterion Δm/σ < 1. In panel D, (top, rastergram) the events are sorted by their theoretical means, with the corresponding spikes rendered alternately in gray and black. Bottom: The histogram obtained from one realization of the data set. The ticks at the bottom represent the theoretical means of the events and are labeled 1 to 8, with the events to be merged shown in a box. (E) Matrix of sROC distances between the events. The events are ordered (the numbers on the x-axis correspond to those in panel D) according to a hierarchical clustering with an sROC threshold of tROC = 0.5. (F) Black curve: The normalized mutual information between the merged events obtained using the sROC criterion and the desired merging. Gray curve: The number of events remaining after merging. The error bars on the mutual information represent the standard deviation across 100 independent realizations of the data set. For the event distribution shown here, the desired merges are not always achieved, because sometimes events 6 and 7 are merged and sometimes events 7 and 8 are merged.