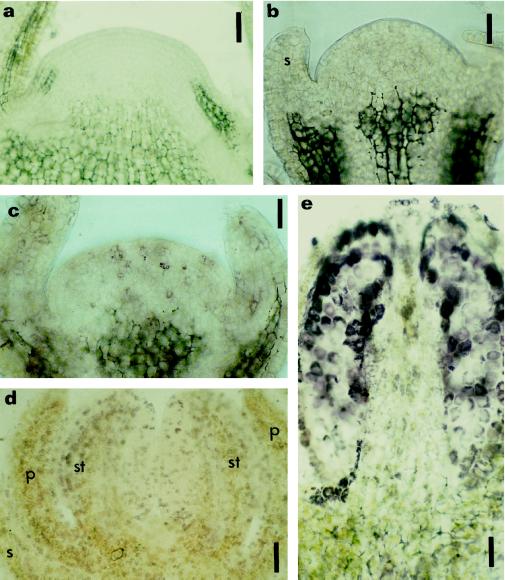
Figure 5.
Immunolocalization of zeatin and IP in prefloral and floral shoot apices. Longitudinal sections of a prefloral transition apex (a), early floral apices (b and c), and floral apices (d and e) subjected to immunohistochemistry for zeatin (a, c, d, and e) and IP (b). Localization was with AP-conjugated secondary antibodies and nitroblue tetrazolium/5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indolyl phosphate as the chromogenic substrate. a, Prefloral transition apex immunostained for zeatin, disclosing no reaction of the AP in the meristem. b and c, Early floral phase with sepal formation showing the absence of label for IP (b), but the presence of reaction with the anti-zeatin antibody was reflected in weak purple staining (c). d and e, Floral phase with sepal, petal, and stamen already initiated; a strong purple staining occurred in different cells throughout the developing flower after immunostaining of zeatin. e, Longitudinal section of a developing stamen immunolabeled with anti-zeatin, showing a strong signal in the sporogenic tissue. p, Petal; s, sepal; st, stamen. Bars = 90 μm (a) and 45 μm (b, c, d, and e).