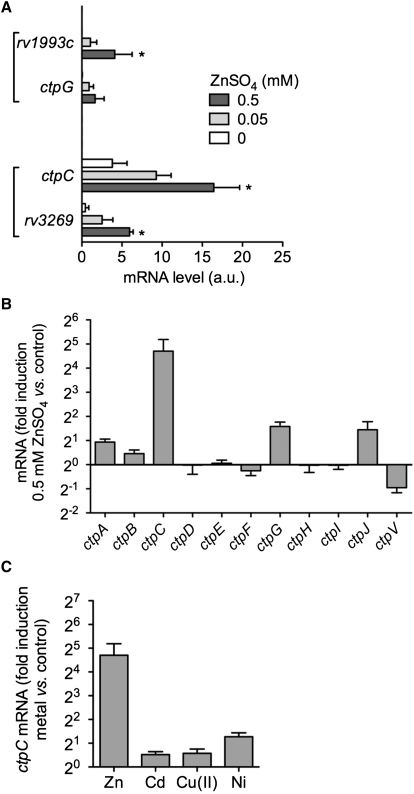
Figure 3.
Expression of the Gene Encoding the M. tuberculosis Metal Cation-Transporting P-Type ATPase CtpC Is Induced by Zinc
(A) Transcriptional profile analysis. mRNA levels (in arbitrary units) of the genes most strongly induced by zinc treatment in M. tuberculosis as revealed by microarray analysis. Bacteria were incubated with 0, 50, or 500 μM ZnSO4 in Sauton medium for 4 hr. Bacterial RNA was prepared for subsequent microarray analysis. The data shown are means ±SD of duplicate experiments and were analyzed with Student's t test; ∗p < 0.05.
(B) RT-qPCR analysis of the expression of the M. tuberculosis ctp genes upon exposure to zinc. Bacteria were incubated with 0 or 500 μM ZnSO4, and RNA extracted and treated as in (A). The data shown are mean ±SD of a triplicate experiment measuring ctp expression, normalized with respect to sigA, in zinc-treated bacteria, relative to untreated bacteria. Data are representative of at least two independent experiments.
(C) RT-qPCR analysis of ctpC expression following the exposure of M. tuberculosis to various divalent metal cations. Bacteria were left untreated or were incubated with 500 μM ZnSO4, 200 nM CdSO4, 500 μM CuSO4, or 200 μM NiSO4 in Sauton medium for 4 hr. The data are shown as in (B) and are representative of two independent experiments.