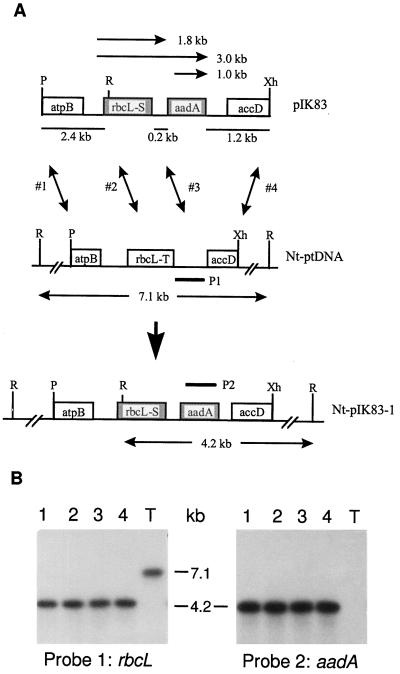
Figure 1.
Targeted replacement of rbcL-T in the tobacco plastid genome with the rbcL-S gene. A, Plastid-targeting region in plasmid pIK83 (plastid DNA is underlined) and the cognate region of the plastid genome (Nt-ptDNA) and of the Nt-pIK83-1 line. atpB (Shinozaki et al., 1986) and accD (Sasaki et al., 1993) are plastid genes. aadA is the plastid-selectable spectinomycin-resistance gene. Recombination endpoints (1–4) discussed in the text are marked by vertical arrows. Horizontal arrows represent mRNAs detected by the rbcL (P1) and aadA (P2) probes. Restriction enzyme recognition sites: P, PvuII; R, EcoRV; Xh, XhoI. B, Wild-type plastid genome copies are absent in four plants regenerated independently (lanes 1–4) from the Nt-pIK83-1 line. Data for wild-type tobacco (T) are also shown. DNA blots of EcoRV-digested total cellular DNA (1 μg per lane) were hybridized with the rbcL (P1) and aadA (P2) probes. The rbcL probe hybridized to a 7.1-kb DNA fragment of the wild-type Nt-ptDNA and a 4.2-kb fragment of the transplastome (Fig. 1A). The 4.2-kb transgenic fragment also hybridized with the aadA probe. Note the lack of wild-type 7.1-kb DNA fragments in the plastid transformants.