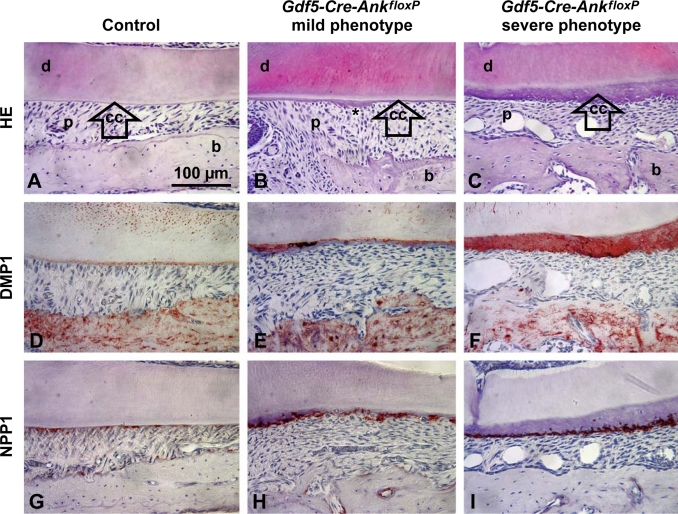
Fig. 8.
Conditional loss of ANK confirms local function in cementogenesis. Compared to control molars (A), conditional KO of Ank in Gdf5-Cre-AnkfloxP resulted in mild phenotypes (B) marked by slight cementum (cc) thickening and local hypercementosis (∗) or severe phenotypes (C) mimicking the global Ank KO. While WT acellular cementum was negative for DMP1 (D), increased DMP1 was found in areas of thickened cementum in mildly affected Gdf5-Cre-AnkfloxP molars (E), and in all cervical cementum in severely affected Gdf5-Cre-AnkfloxP molars (F). WT cementoblasts expressed NPP1 weakly (G), but upregulation was found in cementoblasts of mildly affected Gdf5-Cre-AnkfloxP molars (H), and stronger up regulation in cementoblasts of severely affected Gdf5-Cre-AnkfloxP molars (I). All images are representative examples chosen from the cervical portion of the mesial root of fully developed first molars, with buccal-lingual sectioning used for A, B, D, E, G, and H, and mesial-distal sectioning used for C, F, and I. HE = Hematoxylin-eosin staining. Scale bars in A–I represent 100 μm. d = Dentin; p = PDL; b = bone.