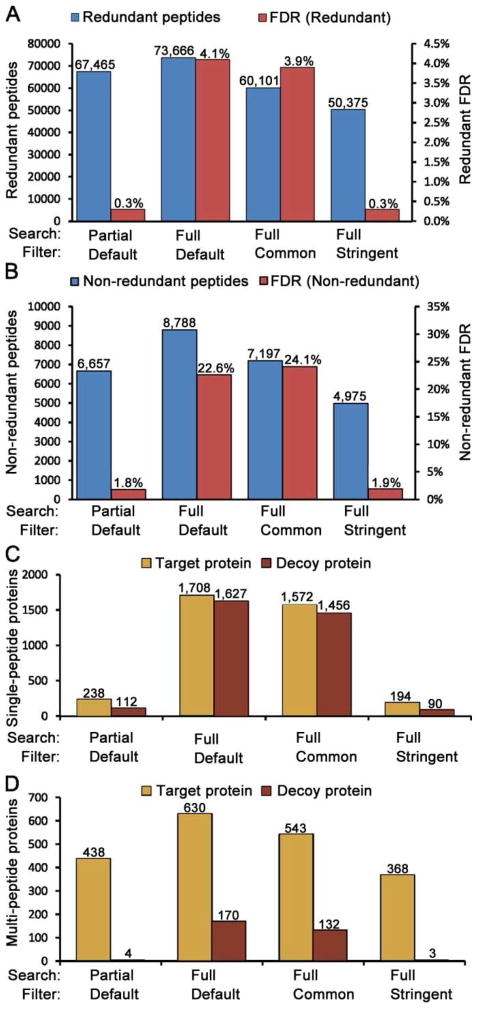
Figure 2. Comparisons of database search and data filtering strategies.
A 40-fraction serum proteome dataset was searched using SEQUEST with either full or partial tryptic boundaries. The resulting identifications were filtered using three alternative conditions (see text). (A) Redundant peptide counts and peptide FDRs. (B) Non-redundant peptide counts and FDRs. (C) Target database and decoy hits for single peptide proteins only. (D) Target database and decoy hits for proteins identified by more than one peptide. These data show that partial tryptic database searches combined with subsequent full tryptic filtering provide both good depth of analysis and high-confidence identifications.