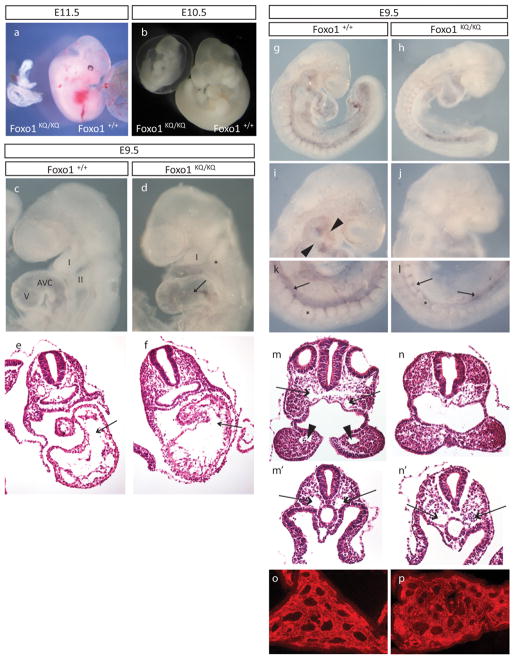
Figure 2. Embryonic lethality in mice homozygous for the Foxo1KQ/KQ mutation.
(A–B) Microphotographs of Foxo1+/+ and Foxo1KQ/KQ embryos at E10.5 and E11.5. (C–D) Microphotographs of E9.5 embryos showing first (I) and second branchial arch (II), as well as atrioventricular canal (AVC) and ventricle (V). Arrow in D indicates the distended AVC in the mutant. (E–F) Histological sections of E9.5 embryos across the AVC (arrows) and ventricle. (G–L) Whole-mount PECAM-1 immunostaining with details of the aortic arch arteries in the head (arrowheads in I, missing in J) and the dorsal aorta (arrows) in the tail region (K–L) of a Foxo1+/+ (G, I, and K) and Foxo1KQ/KQ embryo (H, J, and L). Asterisks in k and l mark somites which are smaller in the mutant. (M–N) Histological sections through the first branchial arch showing dorsal aortae (arrows in M) and the first branchial arch artery (arrowheads in M). (M′-N′) Sections through more posterior regions showing paired dorsal aortae (arrows that are distended in the mutant (N′) compared with wild type (M′). (O–P) Vascular plexus in the yolk sac in Foxo1KQ/KQ and wild type embryos shown by immunostaining for PECAM.