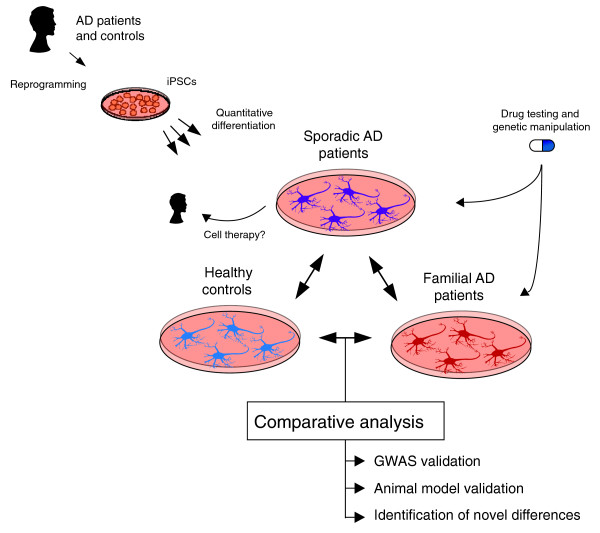
Figure 1.
A general approach for the use of iPSCs to model AD. Samples from sporadic AD patients, familial AD patients and 'healthy' controls are reprogrammed into iPSC lines. iPSCs are then differentiated into cell types of interest, such as neurons, using quantitative methods that compare differentiation efficiency between lines and patients. By comparing iPSC-derived neurons and/or glia between individuals, it may be possible to validate findings from GWAS and animal models studies and to identify novel initiating events of AD. For example, do iPSC-derived neurons from fAD patients have aberrant Aβ secretion? Do iPSC-derived neurons from sAD patients resemble fAD samples?