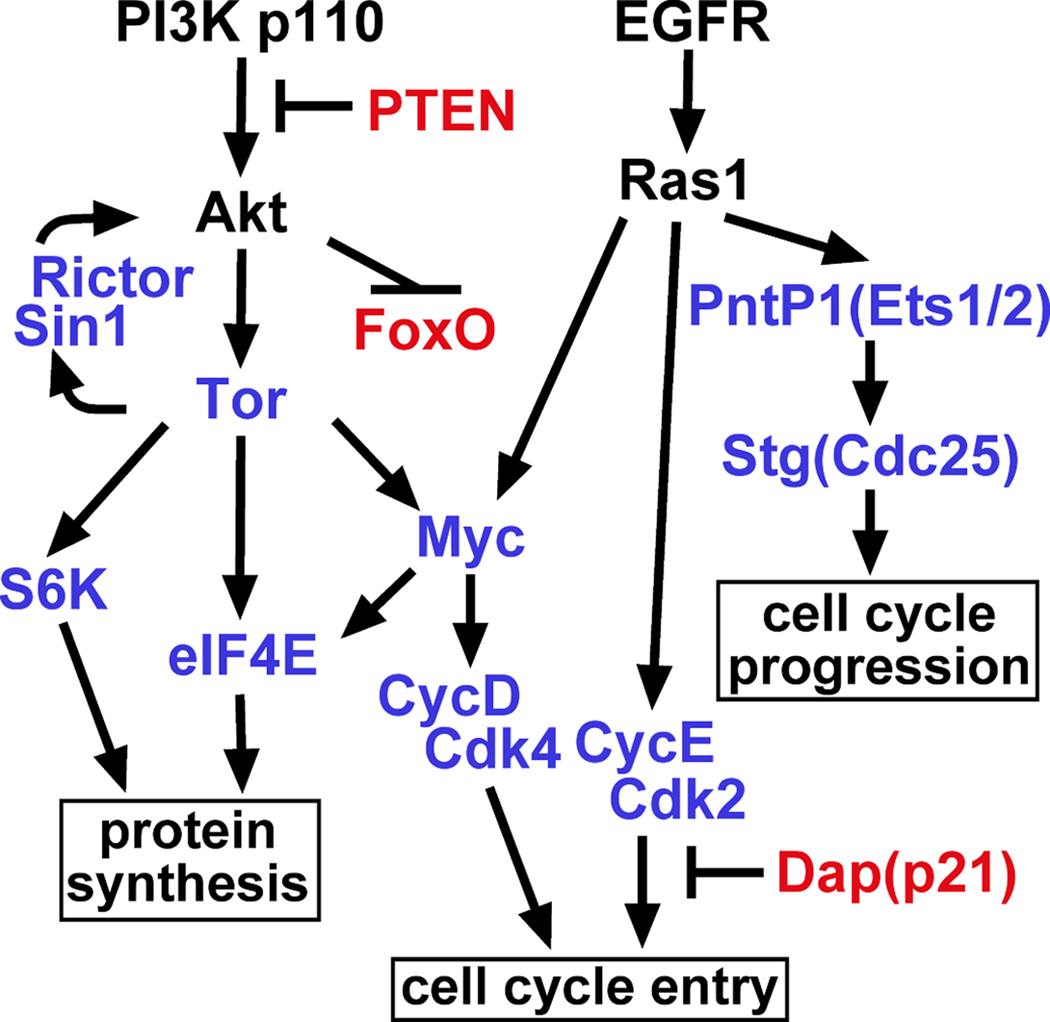
Figure 3. EGFR-PI3K drives glial neoplasia through a combinatorial genetic network.
Pathway diagram of key effectors involved in glial neoplasia initiated by EGFR and PI3K in Drosophila, showing the pathway circuits driving cell cycle entry and progression, and protein translation. Positive regulators are indicated in blue and negative regulators are indicated in red. Arrows indicate pathway connections, although these connections are not necessarily direct. Adapted from (Read et al. 2009).