Figure 2. Hepatic overexpression of cPLA2α suppresses Fas-induced hepatocyte apoptosis and liver tissue damage.
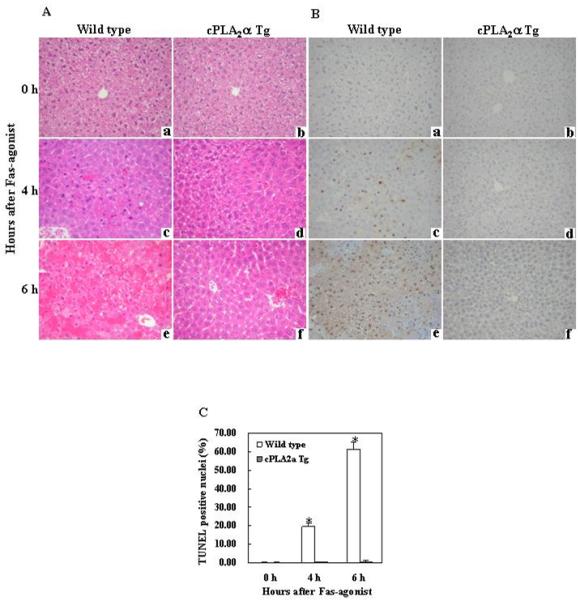
The cPLA2α Tg mice and their age/sex-matched wild type mice were administered intraperitoneally with saline or Jo2 ( 0.5 μg/g body weight ). The animals were sacrificed at 0 (a and b), 4 (c and d) and 6 (e and f) hours after injection and the liver tissues were harvested for histological evaluation. Formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded sections (5 μm thick) were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) (A), and terminal deoxynucleotidy1 – transferase-mediated deoxyuridine triphosphate-digoxigenin nick-end labeling (TUNEL) (B) (200 × ). After Jo2 administration, the livers of the wild type mice exhibit more prominent hemorrhagic necrosis, hepatocyte apoptosis and degeneration (c and e), when compared to the livers of cPLA2α Tg mice (d and f). The number of TUNEL-positive hepatocytes in the wild type mice is significantly higher than in the cPLA2α Tg mice (*p<0.01 compared to the corresponding cPLA2α Tg mice, the data are expressed as mean ±SD from 6 mice) (C).
