Figure 3. Hepatic overexpression of cPLA2α protects the liver from Fas-induced apoptosis.
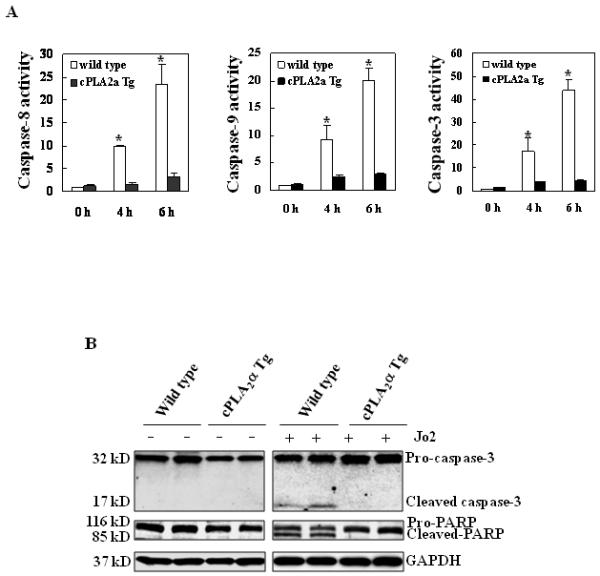
The cPLA2α Tg and their matched wild type mice were administered intraperitoneally with saline or Jo2 (0.5 μg/g body weight). The animals were sacrificed 4 hours after the injection and the liver tissues were harvested and homogenized. (A) The levels of caspases-3, 8, and 9 activities in liver homogenates. Caspase-3, 9, and 8 activities were measured by fluorometric assay with Ac-DEVD-AFC, Ac-LEHD-AFC, and Ac-IETD-AFC as the substrates, respectively. The wild type mice showed higher caspase activities than cPLA2α Tg mice after Jo2 treatment. The results are expressed as mean ±SD of fold changes over wild type livers (*p<0.01 compared to the corresponding cPLA2α Tg mice, n = 6 for each group). (B) Western blot analysis to detect caspase-3 and PARP cleavage. Liver homogenates from the cPLA2α Tg and wild type livers were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis to determine the protein level of proform and cleaved caspase-3 and PARP. Western blot for GAPDH was used as the loading control. Jo2 treatment for 4 hours induced capase-3 and PARP cleavage in the wild type mice, but not in the cPLA2α Tg mice.
