Figure 5. Effects of the cPLA2 inhibitor on Fas-induced hepatocyte apoptosis and liver injury in wild type mice.
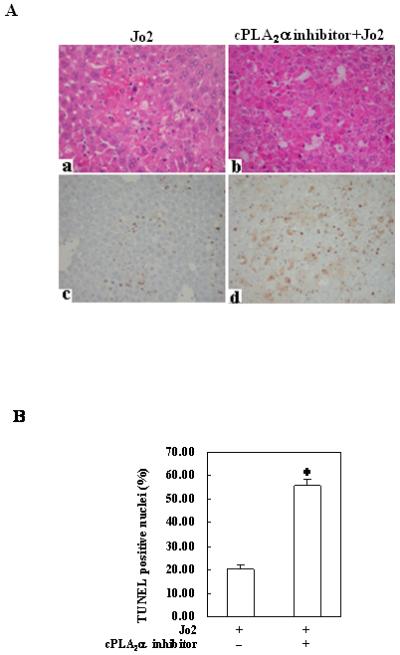
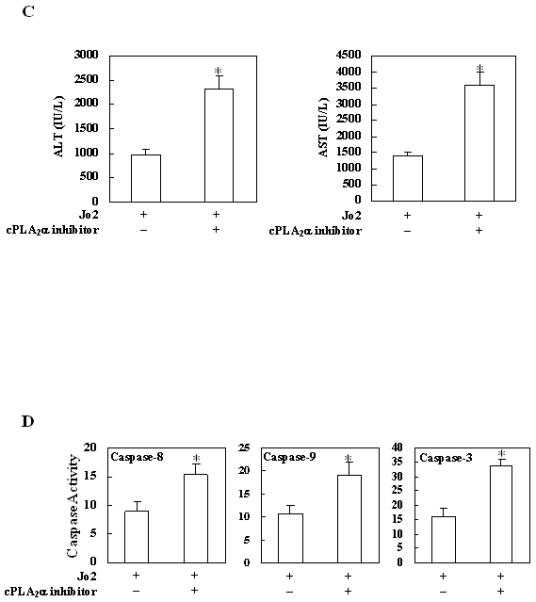
The animals were injected intraperitoneally with the cPLA2α inhibitor pyrrolidine (3 mg/kg body weight) 30 minutes before intraperitoneal administration of Jo2 (0.5 mg/kg body weight). The animals were sacrificed 4 hours after Jo2 injection and the liver tissues were harvested. (A) Representative H&E and TUNEL stains (200×) of the liver tissues from mice pretreated with or without inhibitors (all the mice received Jo2 injection). (B) Quantitation of TUNEL-positive hepatocytes in mice pretreated with or without inhibitors (*p < 0.01 compared to the corresponding wild type mice without inhibitor pretreatment, n = 6 for each group). (C) Serum transaminases. Blood samples were collected at the time of sacrifice and sera were separated for transaminase analysis. Pretreatment of wild type mice with cPLA2 inhibitor induced significantly higher serum ALT and AST levels when compared to pretreatment with vehicle control. The data are expressed as mean ±SD from 6 mice (*p<0.01 vs. corresponding mice pretreated with vehicle, Student’s t test). (D) Caspase activities. The harvested liver tissues were homogenized for subsequent caspase activity assay. Caspase-3, 9, and 8 activities were measured by fluorometric assay with Ac-DEVD-AFC, Ac-LEHD-AFC, and Ac-IETD-AFC as substrate, respectively. Pretreatment with cPLA2 inhibitor induced significantly higher caspase activities than the vehicle control. The results are expressed as mean ±SD of fold changes over wild type livers (*p<0.01 compared to the corresponding mice pretreated with vehicle, n = 6 for each group).
