Fig. 2.
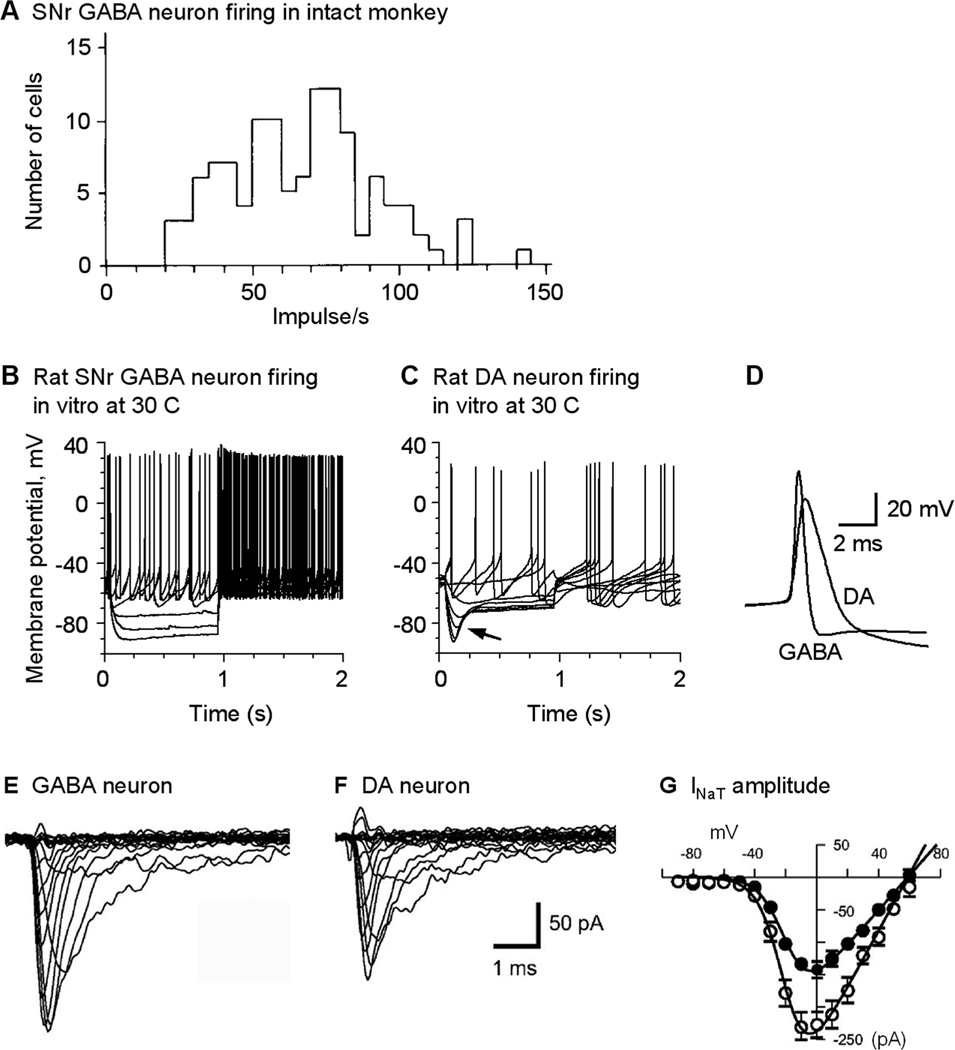
SNr GABA neurons fire sustained spontaneous high frequency spikes. (A) In intact primates, SNr GABA neurons fire tonic high frequency spikes. Modified from Schultz 1986 with permission. (B, C) In isolated preparations with fast synaptic inputs blocked and compared with nigral dopamine neurons, SNr GABA neurons still fire sustained high frequency spikes. In SNr GABA neurons, the Ih is weak whereas it is strong in nigral DA neurons as indicated by the arrow. Modified from Ding et al. 2011 with permission. (D) Spikes in SNr GABA neurons are larger in amplitude and shorter in duration than nigral DA neurons. (E, F, G) SNr GABA neurons have a higher density of the transient voltage-activated sodium current INaT than nigral DA neurons. E–G are modified from Seutin and Engel, 2010 with permission.
