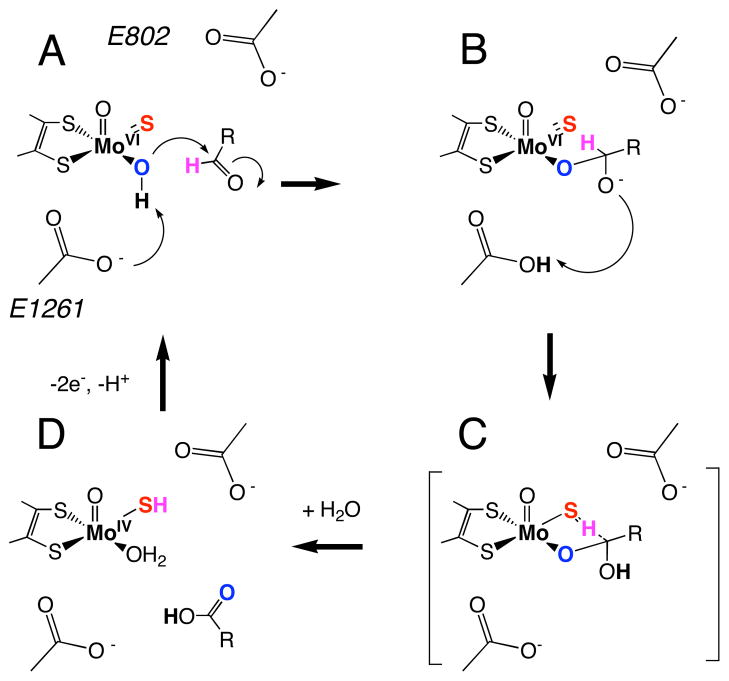
Figure 1.
Proposed reaction mechanism for XO. (A) oxidized active site, (B) tetrahedral intermediate (IM) resulting from nucleophilic attack of metal activated water (i.e. HO−) on aldehyde carbonyl carbon and proton transfer to the general base E1261, (C) putative transition state (TS) showing hydrogen migration between substrate carbon and the terminal sulfido ligand, and (D) the reduced Mo(IV) site following product release and binding of H2O.