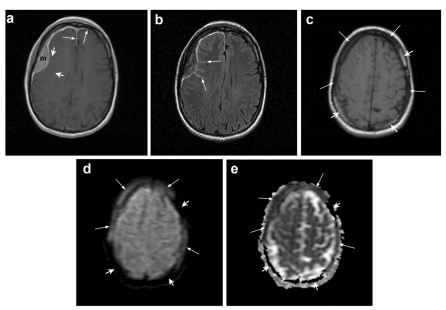
Figure 1.
Brain MR imaging. (a) Post-contrast axial T1-weighted image shows a homogenously enhancing extra-axial dural-based mass (m) in the right frontal region. The thickening and enhancement of the dura extends anteriorly along the falx and along the left frontal lobe (long arrows). There is also subtle enhancement extending into a few of the adjacent cortical sulci (short arrows). (b) Corresponding axial fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) image reveals abnormal hyperintensity within the cortical sulci (arrows) adjacent to the lesion, corresponding to subtle enhancement in A). (c) Non-enhanced axial T1-weighted image at a slightly higher level demonstrates loss of normal bone marrow hyperintensity in the calvarium adjacent to the dural mass and in the left parietal bone (long arrows). Note normal bright bone marrow (short arrows). (d) Corresponding diffusion-weighted image (DWI) reveals signal intensity similar to the dural mass within the affected bone marrow (long arrows). Note normal bone marrow without any signal (short arrows). (e) Corresponding apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map shows that the diffusion of water molecules within the affected bone marrow is similar to the dural lesion (long arrows). Normal bone marrow remains black without any signal (short arrows).