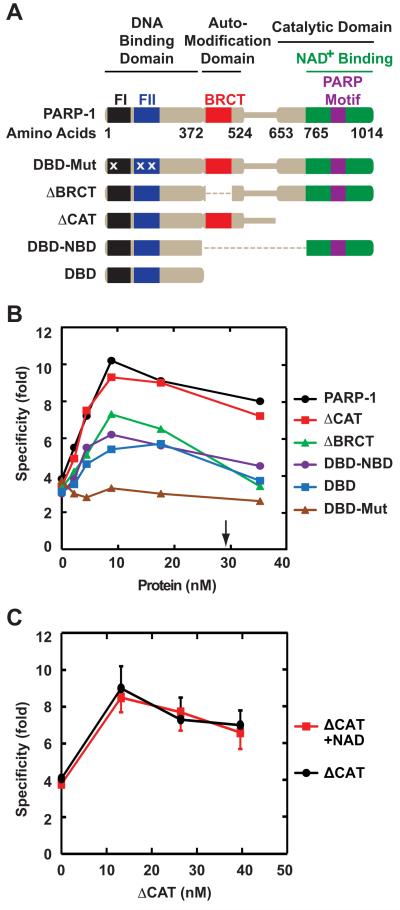
Fig. 3.
Dependence of mismatch repair effects on PARP-1 functional elements. (A) Domain representation of wild-type and mutant forms of PARP-1 is adapted from Wacker et al. [25]. Amino acid substitution mutations within DBD-Mut (C21G in zinc finger FI, C125G and L139P in zinc finger FII) are indicated by the letter X. (B) 5′-directed 4-protein reactions were supplemented with 0 – 35 nM recombinant wild type or mutant PARP-1. Specificity values shown are the mean of three independent determinations. Standard deviation values, which are omitted for clarity, were less than 20% of the corresponding mean values. The arrow indicates the amount of PARP-1 present in 50 μg of nuclear extract. (C) 5′-directed 4-protein reactions were titrated with 0 – 40 nM ΔCAT in the presence or absence of 500 μM NAD+. Results shown are the mean of three determinations ± one standard deviation. For clarity, only plus or minus error bars are shown.