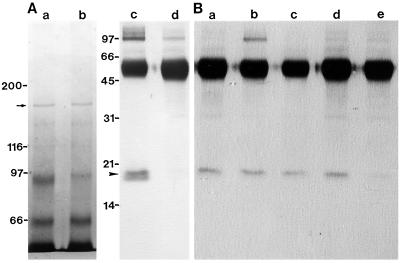
Figure 7.
Immunoprecipitation of 170-kD myosin with antiserum against the 170-kD heavy chain. A, The 170-kD myosin was mixed with the antiserum without (a and c) or with (b and d) 1.5 mm CaCl2 and subsequently mixed with protein A-conjugated beads. Specimens were centrifuged at 500g for 3 min. The materials bound to the beads were analyzed by SDS-PAGE on a 6% polyacrylamide gel (a and b) or by immunoblotting using antiserum against spinach CaM (c and d). B, The 170-kD myosin was mixed with antiserum against the 170-kD heavy chain without the addition of 1.5 mm CaCl2 and subsequently mixed with protein A-conjugated beads. After the beads were washed with KEMP solution containing either EGTA (a) or Ca2+ at concentrations of 10−7 m (b), 10−6 m (c), 10−5 m (d), or 10−4 m (e), the 18-kD polypeptide associated with the beads was detected by the immunoblotting using the antiserum against spinach CaM. The arrow and arrowhead indicate the 170-kD heavy chain and the 18-kD polypeptide, respectively. Mrs (×10−3) of standard proteins are indicated on the left.