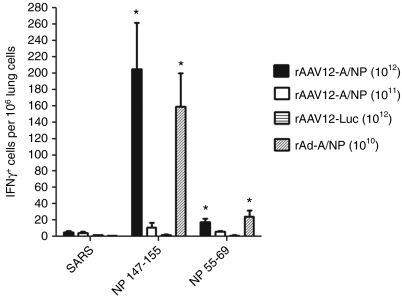
Figure 6.
Detection of T cell response to influenza A/NP peptides in the lungs of recombinant adeno-associated virus type 12 (rAAV12)-A/NP treated animals. Mice were administered either 1 × 1011 or 1 × 1012 rAAV12-A/NP, or 1 × 1012 rAAV12-Luc control vector particles by intranasal (IN) route. Another group received one dose of 1 × 1010 rAd-A/NP by IN administration. Five weeks later rAAV12 mice were boosted IN with the same titer rAAV12 vector. Three weeks post boost, lungs were harvested and interferon (IFN)-γ ELISPOT analysis was performed on individual lung suspensions, where T cell response to stimulation with NP peptides was measured as described in the Materials and Methods section. Negative control for the assay was an irrelevant SARS peptide. Error bars represent the mean IFN-γ producing cells per 106 lung cells + s.e.m., where n = 9 for rAAV12-A/NP high-dose group, n = 5 for rAAV12-A/NP low dose group, n = 5 for the rAd-A/NP group, and n = 4 for rAAV12-Luc group. Statistical comparison was performed by unpaired t-test to compare the response of the high-dose rAAV12-A/NP group and rAd-A/NP group to NP 147–155 and NP 55–69 peptides, with those of the low dose group and rAAV12-Luc control (*P < 0.05).