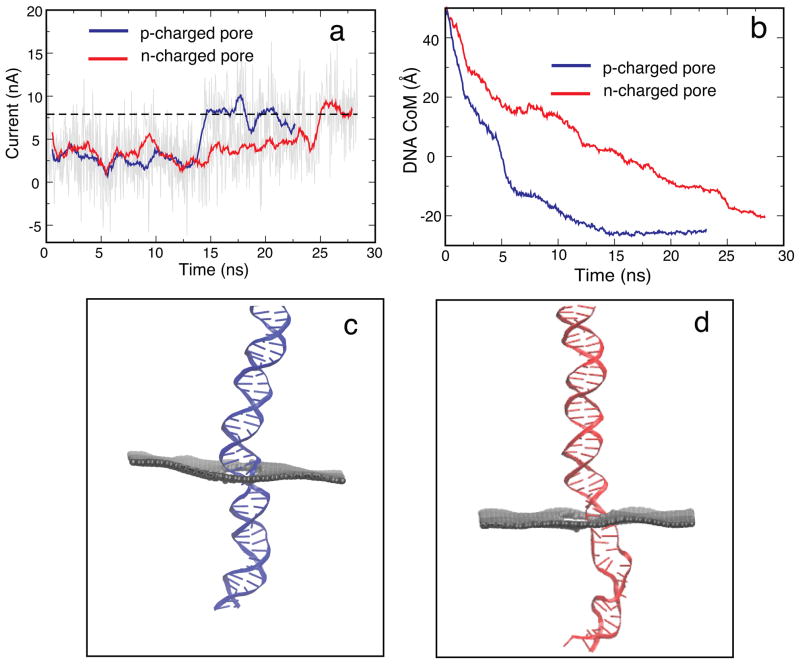
Figure 5.
Effect of pore charges on translocation. (a) Ionic current for p-charged (SimD1) and n-charged (SimD2) pores. (b) Displacement of the DNA center of mass for p- and n-charged pores. (c) Typical configuration of DNA in the p-charged pore. (d) Typical configuration of DNA in the n-charged pore. DNA in the n-charged pore adopts a more stretched conformation than in the p-charged pore (The geometrical diameter of the pore is 2.4 nm, the bias voltage is 1 V and the total charge on the pore mouth is ± 3.6 e).