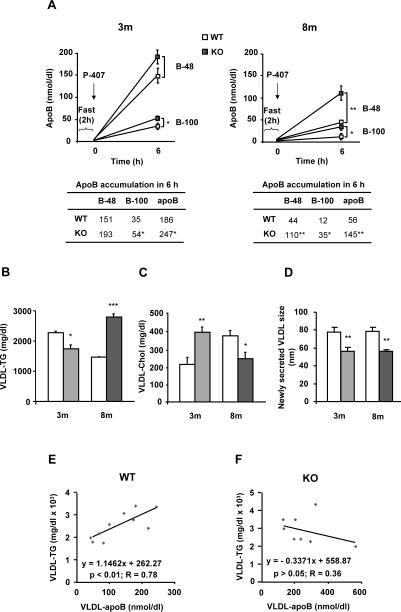
Fig. 2. MAT1A deletion increases the rate of VLDL-apoB secretion and impairs VLDL-lipid output in mice.
3-month-old (3m) and 8-month-old (8m) wild type (WT) (□) and MAT1A-knockout (MAT1A-KO) ( ) mice were fasted 2 hours prior to the injection of 1 mg/g poloxamer (P-407) in saline to inhibit VLDL metabolism. Before P-407 injection and 6 hours later, blood was collected and VLDL (d<1.02 g/ml) were isolated from serum by ultracentrifugation and characterized for apoB48, apoB100, triglyceride (TG) and cholesterol (Chol) content and particle size. (A) VLDL-apoB48 (B-48) and VLDL-apoB100 (B-100) mass is represented before and after injection. (B) TG and (C) cholesterol levels were determined in VLDL 6 hours after P-407 injection and corrected with their levels at zero time. (D) Diameters of newly secreted VLDL were measured by dynamic light scattering. For that, hepatocytes isolated from 3m and 8m mice by collagenase digestion were cultured for 24 hours and VLDL isolated from the culture medium. (E, F) Correlation studies were carried out by using Pearson's correlation coefficient and significance was defined as p<0.05. Values are means ± SEM of 4–8 animals per group. Statistical differences between MAT1A-KO and WT mice are denoted by *p<0.05, **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 (Student's t test).
) mice were fasted 2 hours prior to the injection of 1 mg/g poloxamer (P-407) in saline to inhibit VLDL metabolism. Before P-407 injection and 6 hours later, blood was collected and VLDL (d<1.02 g/ml) were isolated from serum by ultracentrifugation and characterized for apoB48, apoB100, triglyceride (TG) and cholesterol (Chol) content and particle size. (A) VLDL-apoB48 (B-48) and VLDL-apoB100 (B-100) mass is represented before and after injection. (B) TG and (C) cholesterol levels were determined in VLDL 6 hours after P-407 injection and corrected with their levels at zero time. (D) Diameters of newly secreted VLDL were measured by dynamic light scattering. For that, hepatocytes isolated from 3m and 8m mice by collagenase digestion were cultured for 24 hours and VLDL isolated from the culture medium. (E, F) Correlation studies were carried out by using Pearson's correlation coefficient and significance was defined as p<0.05. Values are means ± SEM of 4–8 animals per group. Statistical differences between MAT1A-KO and WT mice are denoted by *p<0.05, **p<0.01 and ***p<0.001 (Student's t test).