Fig. 7.
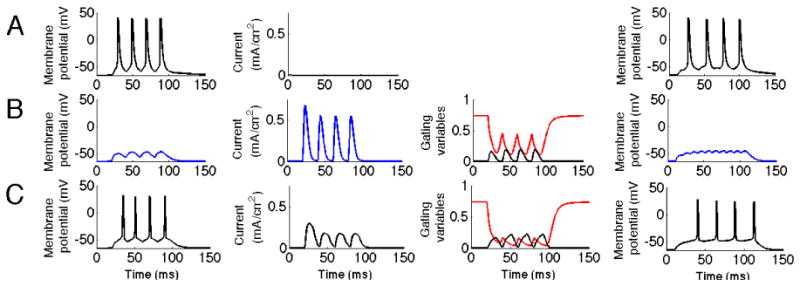
KA reduces response to fast ripple input. The three first columns correspond to the simulation when the input frequency was 50 Hz and the fourth column a case with 100Hz input. The first column represents the membrane potential of the soma. The second column represents the current through the KA channel measured at the location of the synaptic input. The third column represents the gating variables of the KA channel. The black line represents the activation and the red line inactivation.A. Fast ripple input with no KA present. B. Fast ripple input with KA present. Note the significant reduction in spike activity. It can be seen that the inactivation is lower than in the control case C, particularly in its troughts. C. Ripple input. KA does not suppress input representing ripple activity.
