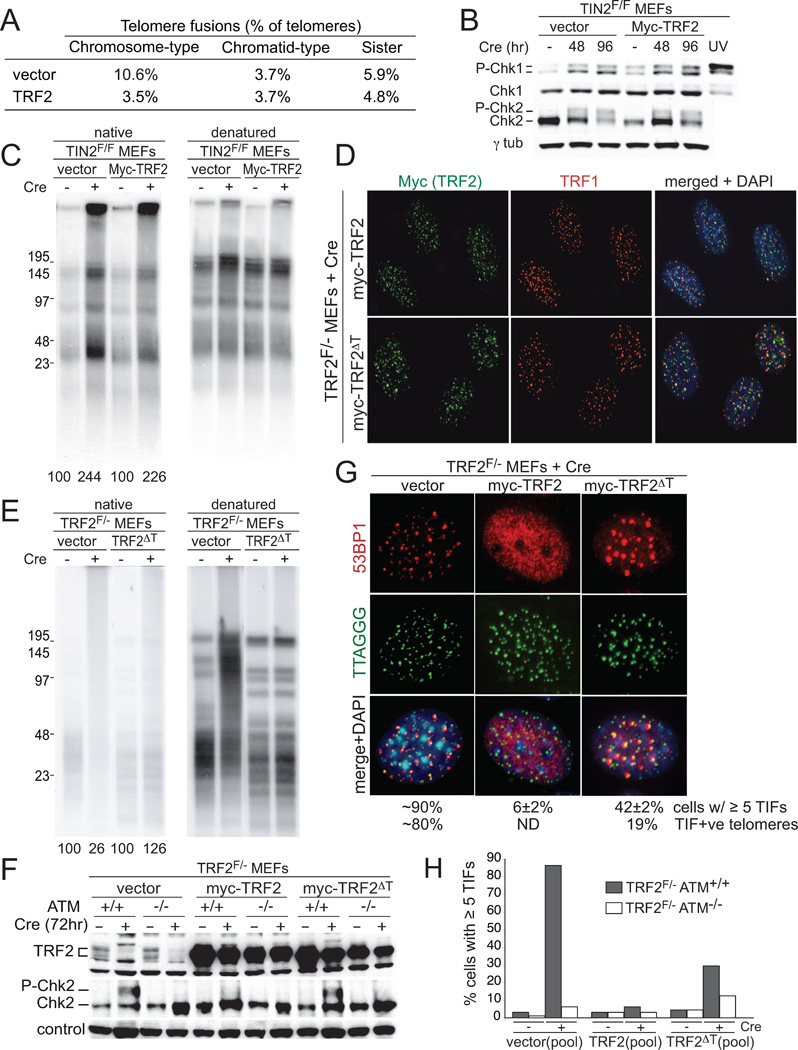
Figure 6. TRF2 requires TIN2 for repression of ATM but not NHEJ.
(A) Overexpression of TRF2 reduces chromosome-type fusions in TIN2 KO cells. Telomere fusions were scored as in Figs. 3E and F. (B) Immunoblots for Chk1 and Chk2 phosphorylation. Cells as in (A) and processing as in Fig. 4B. (C) No effect of TRF2 overexpression on telomeric overhang in TIN2 KO cells. Cells as in (A) and processing and quantification as in Fig. 3A. (D) Telomeric localization of the TRF2ΔT mutant. TRF2F/−MEFs were infected with the indicated TRF2 alleles, selected, cloned, and treated with Cre. TRF2 was detected with the Myc Ab in combination with IF for TRF1. (E) Repression of telomere fusions by TRF2ΔT. Cells as in D were analyzed at 120 hr post-Cre as in Fig. 3A. (F) Chk2 phosphorylation in TRF2ΔT cells. TRF2F/−ATM+/+ and TRF2F/−ATM−/− cells were infected with the indicated retroviruses, selected, and treated with Cre as indicated. Immunblotting for Chk2 and TRF2 at 72 hr post-Cre. Loading control: non-specific band in the Chk2 blot. (G) TIFs in TRF2ΔT cells. The indicated clonal lines (as in (D)) were treated with Cre (96 h) and analyzed for TIFs as in Fig. 4A. Note fewer but larger 53BP1 TIFs in TRF2ΔT cells. (H) Quantification of the TIF response in the indicated cells at 96 hr after Cre. Pools of TRF2F/− ATM+/+ and TRF2F/−ATM−/− infected as indicated were used for TIF assays as in Fig. 4A.