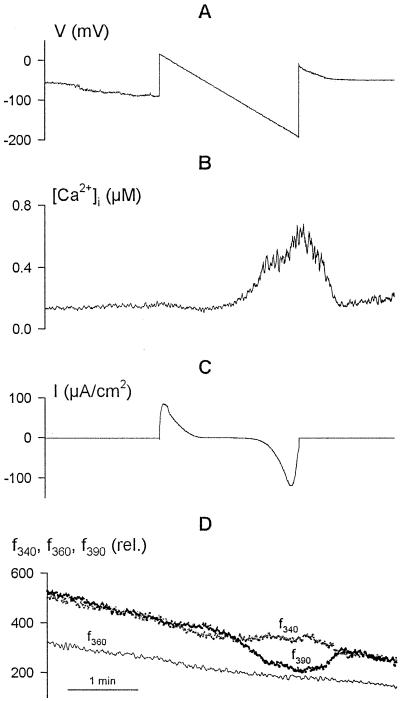
Figure 1.
Voltage ramps demonstrate a voltage threshold for increases in [Ca2+]i and consequent inactivation of current carried by IK,in. Concurrent records of voltage (A), [Ca2+]i (B), and clamp current (C) are shown, along with the raw Fura-2 fluorescence recorded on f340, f360, and f390 (D). Data are from one guard cell bathed in 5 mm Ca2+-Mes, pH 6.1, with 10 mm KCl. Slowly ramping membrane voltage from +20 to −200 mV under voltage clamp was accompanied by an appreciable rise in [Ca2+]i at voltages negative of about −120 mV. The outward (positive) current at the start of the voltage ramp is associated with IK,out (Blatt and Grabov, 1997). Activation of inward (negative) current at voltages negative of −120 mV, carried predominantly by IK,in (Blatt and Grabov, 1997), was followed by a near-complete decay in current amplitude during the final 10 s of the ramp and coincident with the [Ca2+]i rise near and above 400 nm. Gradual decay in fluorescence recorded on excitation at all three wavelengths (D) is characteristic of progressive photobleaching of Fura-2 under these conditions. Note the absence any influence of the voltage ramp on the fluorescence trajectory recorded at the isobestic wavelength f360.