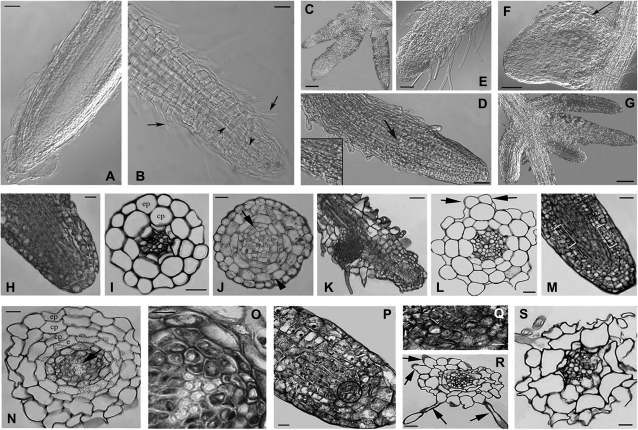
Fig. 4.
The effects of Cd treatments on root anatomy of wild-type, AtPCSox-5, and AtPCSox-1 seedlings. Nomarski DIC images (A–G), and histological images (H–S) of wild-type and AtPCSox roots from seedlings treated for 9 d with different concentrations of CdSO4. (A) Regular morphology of wild-type roots in seedlings treated with 30 μM CdSO4. (B) Root showing precocious xylem differentiation in the elongation zone (arrowheads) and abundant hair formation (arrows) in wild-type seedlings treated with 60 μM CdSO4. (C) Irregular lateral root branching in wild-type seedlings treated with 90 μM CdSO4. (D) Abundant hair formation and xylem differentiation up to the apex (arrow and inset) in the root of AtPCSox-1 seedlings treated with 30 μM CdSO4. (E) Very high production of root hairs up to the apex, and a reduction in cap extension in AtPCSox-1 seedlings treated with 60 μM CdSO4. (F) Anomalous shape of a lateral root primordium due to irregular proliferation of the cortical cells (arrow) in AtPCSox-5 seedlings treated with 60 μM CdSO4. (G) Irregular lateral root branching of AtPCSox-5 seedlings treated with 90 μM CdSO4. (H) Normal histological structure of a wild-type root apex (longitudinal section, 30 μM CdSO4 treatment). (I) Normal histological structure of a wild-type root apex (transection, 30 μM CdSO4 treatment). (J) Hypertrophy in the cortical parenchyma (arrowhead) and perycicle proliferation (arrow) of a wild-type root near the apex (transection, 60 μM CdSO4 treatment). (K) Anomalous position of a lateral root primordium in a wild-type primary root (longitudinal section, 60 μM CdSO4 treatment). (L) Anomalous trichoblast differentiation (arrows) in a wild-type root (transection, 60 μM CdSO4 treatment). (M) Anomalous proliferation and expansion of cells committed to differentiate cortical parenchyma, endodermis, and pericycle in an AtPCSox-1 root apical meristem (rectangles) (longitudinal section, 30 μM CdSO4 treatment). (N) Doubling of the cortical parenchyma and aboundant xylem differentiation (arrow) in an AtPCSox-1 root (transection, 60 μM CdSO4 treatment). (O) Detail of the stelar region in a primary root, showing xylem overproduction at higher magnification. (P) AtPCSox-5 primary root apex showing the proliferation of initial cells around the quiescent centre (circle) (longitudinal section, 60 μM CdSO4 treatment). (Q) The proliferating zone at higher magnification. (R) Anomalous root hairs (arrows) differentiated in an AtPCSox-5 root (transection, 60 μM CdSO4 treatment). (S) Epidermal and cortical cells anomalous in shape in an AtPCSox-5 root (transection, 90 μM CdSO4 treatment). Sections from (H) to (S) were stained with toluidine blue. Bars: 10 μm (I, J, L, N–Q), 20 μm (H, R, S), 25 μm (M), 50 μm (A, B, E, F, D, K), 100 μm (C, G); e, endodermis; cp, cortical parenchyma; ep, epidermis.