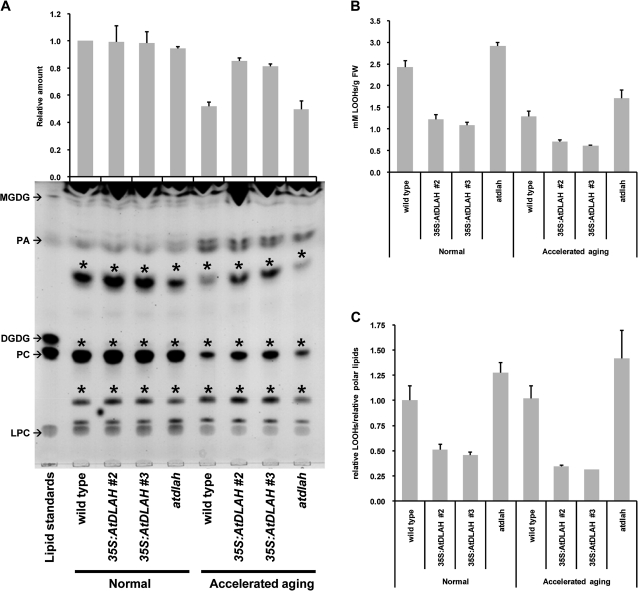
Fig. 7.
Lipid peroxidation and lipid content in wild-type, AtDLAH-overexpressing T4 transgenic, and atdlah mutant seeds. (A) Total lipid content in wild-type, AtDLAH-overexpressing (lines #2 and #3), and atdlah mutant seeds under normal and accelerated-ageing conditions. Total polar lipids were separated by TLC and visualized with iodine vapour. The lipid standards from top to bottom are MGDG, PA, DGDG, PC, and LPC. The amounts of individual polar lipids (represented above the plate) were quantified from the TLC plates using Multi Gauge v.3.1 (Fuji Film, Tokyo, Japan). The lipid bands which showed the detectable differences in intensity on the TLC plate among wild-type, 35S:AtDLAH, and ataldh are indicated by asterisks (*). Results are expressed as means ±SD from three independent experiments. (B) Absolute levels of lipid hydroperoxide in wild-type, AtDLAH-overexpressing (lines #2 and #3), and atdlah mutant seeds under normal and accelerated-ageing conditions. The levels of lipid hydroperoxides (LOOHs) were measured by FOX assay. The different amounts of H2O2 were used for generating a standard curve and the amount of LOOH in seeds was calculated as a H2O2 level. LPC (40 μg) was used as a control for lipid extraction from each seed sample. Results are expressed as means ±SD from three independent experiments. (C) Relative levels of LOOHs per polar lipid in wild-type, AtDLAH-overexpressing (lines #2 and #3), and atdlah mutant seeds under normal and accelerated-ageing conditions. Each ratio was calculated by dividing the amount of LOOH by the relative amount of polar lipids. Results are expressed as means ±SD from three independent experiments.