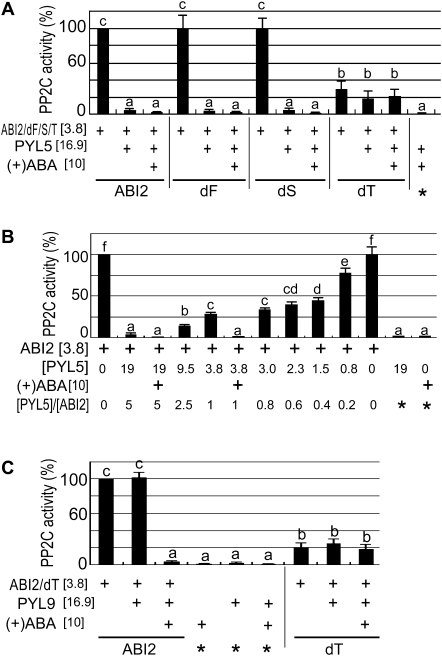
Fig. 4.
Deletion mutation of the third CDPK phosphorylation site-like motif of ABI2 reduces the catalytic activity and abolishes the response of ABI2 to the ABA receptors PYL5 and PYL9 in vitro. (A) Deletion mutation of the third CDPK phosphorylation site-like motif (CPL) of ABI2 (dT), but not the deletion mutations of the first (dF) and second (dS) CPL, reduces the catalytic activity and abolishes the response of ABI2 to the ABA receptor PYL5 in vitro. The concentrations of ABI2/dF/dS/dT protein, PYL5 protein, and (+)ABA in the reaction medium are indicated in square brackets (unit: μM). (B) PYL5 inhibited the ABI2 activity in a dose-dependent manner in the absence of ABA, but ABA can improve the inhibitory effect of PYL5 on ABI2 activity. The PYL5 protein at different concentrations (indicated by [PYL5], unit: μM) was added to the PP2C-assaying medium to investigate the PYL5 dose dependence. The concentration of ABI2 or (+)ABA in the reaction medium is indicated in square brackets (unit: μM). The ratios of the concentrations of PYL5 to ABI2 are shown (indicated by [PYL5]/[ABI2]). (C) ABI2 deletion mutation form dT reduces the catalytic activity and abolishes the response of ABI2 to the ABA receptor PYL9 in vitro. The concentrations of ABI2/dT protein, PYL9 protein, and (+)ABA in the reaction medium are indicated in square brackets (unit: μM). In A–C, wild-type ABI2 protein is indicated by ABI2. Addition of the proteins (or 10 μM ABA) listed on the left to the PP2C-assaying system is indicated by a plus sign (+). Several controls were used and are marked by asterisks (*). Relative PP2C activities (%) were used, which were normalized relative to that of the wild-type ABI2 in the absence of PYL5/9 and ABA, which was taken as 100% with a value of ∼3.3 nmol min−1 mg−1 PP2C. Each value is the mean ±SE of five independent biological determinations, and different letters indicates significant differences at P <0.05 (Duncan's multiple range test).