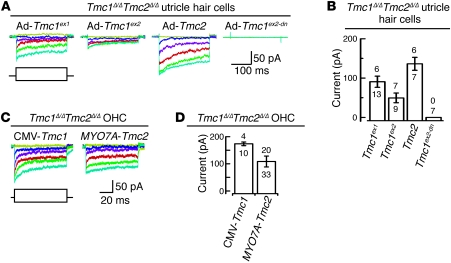
Figure 7. Rescue of mechanotransduction with Tmc1 or Tmc2.
(A) Organotypic cultures of utricles harvested at P0–P3 from Tmc1Δ/ΔTmc2Δ/Δ mice were exposed to adenoviral vectors expressing Tmc1ex1 (n = 4 mice), Tmc1ex2 (n = 3 mice), Tmc2 (n = 5 mice), or Tmc1ex2-dn (n = 3 mice) and maintained in culture for 2–4 days. Scale bars apply to all current families. The envelope of the stimulus protocol is shown at the bottom left. (B) For each bar, the upper number indicates the number of cells with measurable mechanotransduction currents, while the lower number indicates total number of tested cells. Mean maximal currents are plotted from cells with measurable current (±SEM). (C) Organotypic cultures of cochleae were harvested from Tmc1Δ/ΔTmc2Δ/Δ mice at P0. Representative mechanotransduction current families for cochlear OHCs transfected with CMV promoter–driven Ad-Tmc1ex1 (n = 4 mice) or MYO7A promoter–driven Ad-Tmc2 (n = 11 mice). Ad-Tmc1ex1 or Ad-Tmc2 rescue mechanotransduction in Tmc1Δ/ΔTmc2Δ/Δ OHCs. Scale bars apply to both current families. The envelope of the stimulus protocol is shown at the bottom left. (D) Summary bar graph shows mean maximal mechanotransduction current amplitudes (±SEM) from 43 RFP-positive (transfected) OHCs. For each bar, the upper number indicates the number of cells with measurable mechanotransduction currents, while the lower number indicates total number of cells examined.