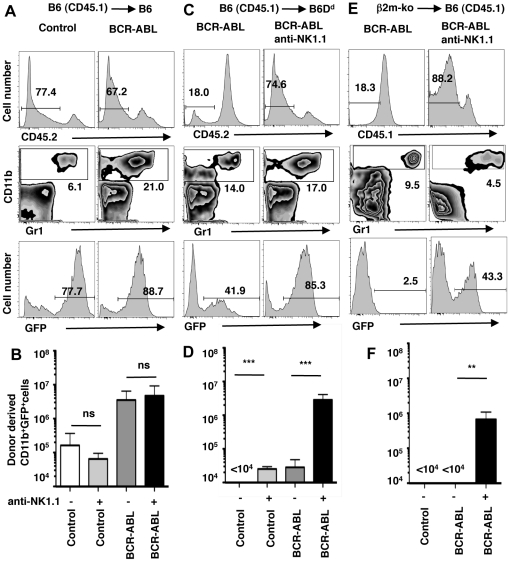
Figure 1. NK cell mediated missing-self recognition reduces the expansion of BCR-ABL1+ myeloid cells in vivo.
BM cells from 5-FU treated B6 mice (H-2b, CD45.1) were transduced with retroviral vectors encoding GFP (Control) or BCR-ABL1 plus GFP (BCR-ABL1) followed by transplantation into lethally irradiated, MHC-I matched B6 (H-2b, CD45.2) mice (A, B) or MHC-I-different B6 Dd mice (H-2bDd, CD45.2) (C, D). In addition, BM cells from 5-FU treated β2m-deficient (β2m-ko) mice (MHC-Ilow, CD45.2) were transduced with retroviral vectors encoding BCR-ABL1 plus GFP followed by transplantation into B6 (H-2b, CD45.1) mice (E, F). Some recipient mice had been depleted of NK1.1+ cells by the injection of mAb PK136 (anti-NK1.1). Histograms show the identification of donor-derived cells at day 8 after transplantation (upper panel). Donor-derived cells were further analyzed for the presence of myeloid cells (CD11b+)(middle panel) and GFP expression in donor-derived myeloid cells (lower panel). Numbers indicate the percentage of cells in the respective gate. Bar graphs show the mean absolute number (±SD) of donor-derived myeloid cells expressing GFP (either control or BCR-ABL1) in recipient spleens at day 8 after transplantation. Donor-recipient mouse strain combinations were (B) B6 (H-2b, CD45.1)->B6 (H-2b, CD45.2) (MHC-I identical) and (D) B6 ((H-2b, CD45.1) into B6Dd (H-2bDd, CD45.2) (MHC-I different, partial missing-self) and (F) β2m-ko (MHC-1low, CD45.2)−>B6 (H-2b, CD45.1) (MHC-I deficient, complete missing-self). The significance of the difference between indicated data sets is depicted as *** p<0.001, ** p<0.01 and ns not significantly different p>0.05.