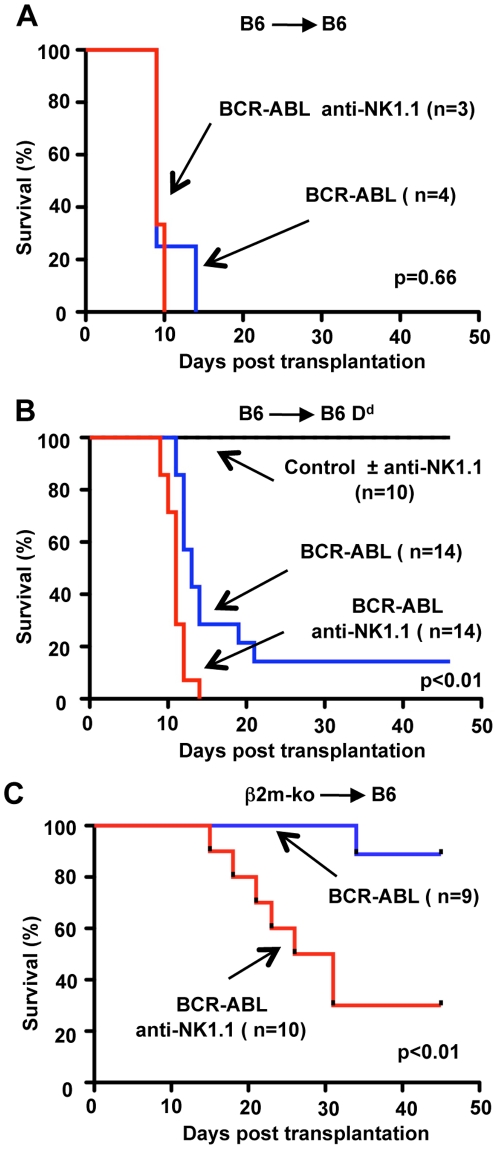
Figure 4. NK cell-mediated missing-self recognition can protect from BCR-ABL1 induced CML disease.
A Survival graph of B6 recipients (H-2b) transplanted with a mixture of BCR-ABL1 transduced B6 BM cells (H-2b) and non-transduced B6 rescue BM (H-2b). Some recipient mice had been depleted of NK1.1+ cells by the injection of mAb PK136 (anti-NK1.1). These data are derived from a single experiment. B Survival graph of B6Dd recipients (H-2bDd) transplanted with mixtures of control transduced B6 BM (H-2b) and non-transduced B6Dd rescue BM (H-2bDd). All recipient mice survived independent of the presence or absence of NK1.1+ cells (±anti-NK1.1). Survival of B6Dd recipients (H-2bDd) transplanted with mixtures of BCR-ABL1 transduced B6 BM (H-2b) and non-transduced B6Dd rescue BM (H-2bDd). In the presence of NK cells, the survival of recipients is significantly improved (p<0.01). The data have been compiled from three independent experiments. C Survival graph of B6 recipients (H-2b) transplanted with mixtures of BCR-ABL1 transduced β2m-ko (MHC-Ilow) BM and non-transduced B6 rescue BM (H-2b). In the presence of NK cells, the survival of recipients is significantly improved (p<0.01). The data have been compiled from two independent experiments.