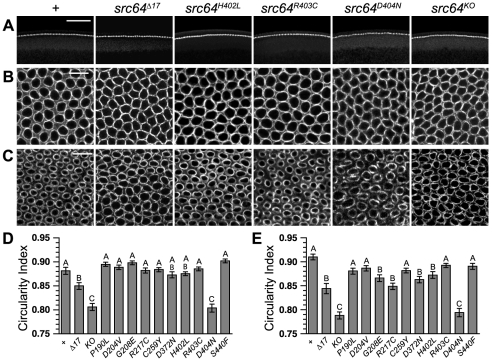
Figure 3. Cellularization microfilament defects in src64 mutant embryos.
Embryos are stained with antibody to myosin II heavy chain. (A) Cross-sections showing the early cellularization front. Furrow canal depths are less uniform, producing a wavy and irregular cellularization front in src64Δ17, src64H402L, src64D404N and src64KO mutant embryos. Scale bar, 50 µm. (B) Grazing section projections of early cellularization stage embryos showing the microfilament network. Microfilament rings of src64Δ17, src64H402L, src64D404N and src64KO mutant embryos are irregular. Scale bar, 10 µm. (C) Grazing section projections of late cellularization stage embryos showing microfilament rings. Microfilament rings of src64Δ17, src64H402L, src64D404N and src64KO mutant embryos are irregular and less constricted than the microfilament rings of wild-type embryos and src64R403C mutant embryos. Scale bar, 10 µm. (D) Microfilament ring circularity during early cellularization. A, does not differ from +; AB, differs from + and src64Δ17; B, does not differ from src64Δ17 allele but differs from + (P<0.01); C, does not differ from src64KO but differs from + (P<0.001) and src64Δ17 (P<0.001). Error bars are SEM. (E) Microfilament ring circularity during late cellularization. A, does not differ from +; B, does not differ from src64Δ17 but differs from + (P<0.05); C, does not differ from src64KO but differs from + (P<0.001) and src64Δ17 (P<0.001). Error bars are SEM.