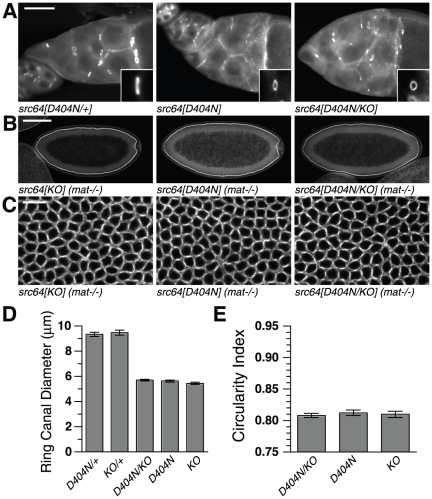
Figure 5. Cytoskeletal defects of src64D404N/src64KO trans-heterozygotes.
(A) src64D404N/+, src64D404N and src64D404N/src64KO egg chambers stained with antibody to HTS. Ring canal diameters are not reduced in src64D404N/+ egg chambers but are reduced in src64D404N/src64KO egg chambers. Inset: ring canal of approximately mean diameter, reoriented so that diameter is projected along the vertical axis. Scale bar, 50 µm. (B) Early cellularization stage embryos laid by src64KO, src64D404N and src64D404N/src64KO mothers. Embryos show non-uniform cellularization fronts. Scale bar, 100 µm. (C) Grazing section projections of early cellularization stage embryos laid by src64KO, src64D404N and src64D404N/src64KO mothers showing microfilament networks. Microfilament ring defects of maternally trans-heterozygous src64D404N/src64KO embryos are similar to those of src64KO and src64D404N embryos. Embryos are stained with antibody to myosin II heavy chain. Scale bar, 10 µm. (D) Ring canal diameters. src64D404N and src64D404N/src64KO do not differ (p = 0.35). Error bars are SEM. (E) Microfilament ring circularity during early cellularization. src64D404N and src64D404N/src64KO do not differ (p = 0.52). Error bars are SEM.