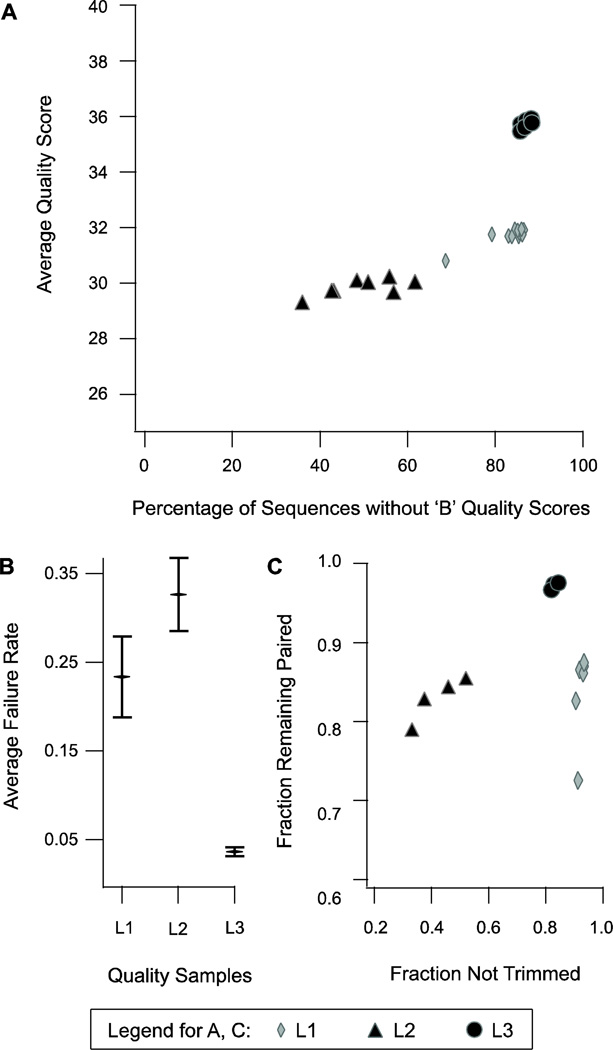
Figure 1. Raw Read Quality Statistics.
A comparison of quality metrics regarding quality filtration of raw reads in the samples L1, L2, and L3. A) The samples L1, L2, and L3 have 6, 4 and 3 components respectively, each of which was sequenced in a separate lane in a flow cell and each of which has a set of forward reads and paired reverse reads in separate files. Each forward and reverse read file is represented by a marker indicating the sample set to which it belongs, and is at a position indicating the average quality score and percentage of sequences without a ‘B’ quality score of the reads in that file. B) The failure rates in the components of each sample set are shown by a marker at the mean with error bars indicating one standard deviation above and below. C) The fraction of reads that remain paired and those that did not need to be trimmed are indicated for each component in a sample set. The legend at the bottom indicates the meanings of marker types in A and C.